HPLC Method for Separation of Histidine, Histidine Methyl Ester, and Histidine Lauryl Ester on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
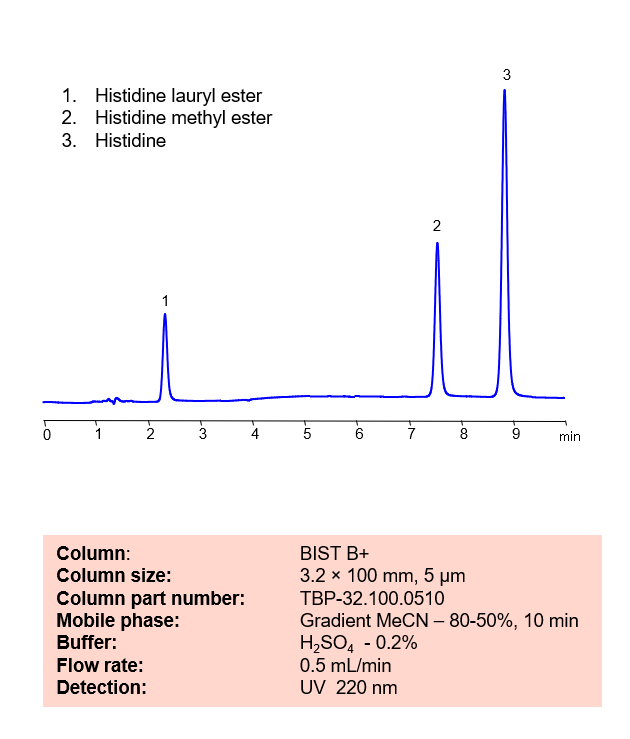
Histidine is a naturally occurring essential amino acid that the body uses to repair damaged tissue and generate new blood cells. Histidine Methyl Ester is a histidine decarboxylase inhibitor and can be used to synthesize other biological compounds. Histidine Lauryl Ester is another derivative of Histidine. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, Histidine and its derivatives can be retained and separated on a positively charged, anion-exchange BIST™ B+ column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, negative buffer, such as Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which acts as a bridge, linking the positively charged dipeptide to the positively charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, Histidine and its derivatives can be UV detected at 220 nm.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Histidine, Histidine Methyl Ester and Histidine lauryl Ester
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 3.2 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN – 80 – 50%, 10 min |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 220 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 2.2 min, 7.5 min, 8.9 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Histidine methyl ester, Histidine |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Histidine methyl ester





