HPLC Method for Analysis of DAPI on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies
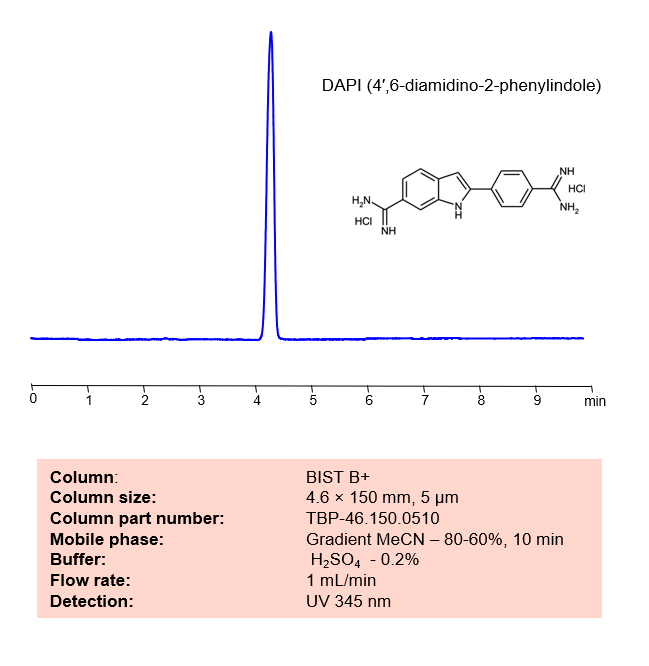
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, also known as DAPI, is a fluorescent dye with the chemical formula
C16H15N5. It is often used for DNA staining and fluorescence microscopy. Under ultraviolet (UV) and upon binding, it emits light in the blue portion of the spectrum (461 nm for DNA and ~500 nm for RNA).
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, DAPI (dihydrochloride) can be retained on a positively-charged anion-exchange BIST™ B+ column.
There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, negative buffer, such as Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which acts as a bridge, linking the positively-charged analytes to the positively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting of a majority of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Utilizing a step gradient to switch to a completely aqueous MP after 2 minutes allows for retention to occur while also preventing the method from being too long. Using this new and unique analysis method, DAPI (dihydrochloride) can be separated, retained, and UV detected at 345 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 345 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 4.01 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Dye |
| Analyzing Compounds | DAPI (dihydrochloride) |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





