Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Oligonucleotides on BIST AC Column by SIELC Technologies
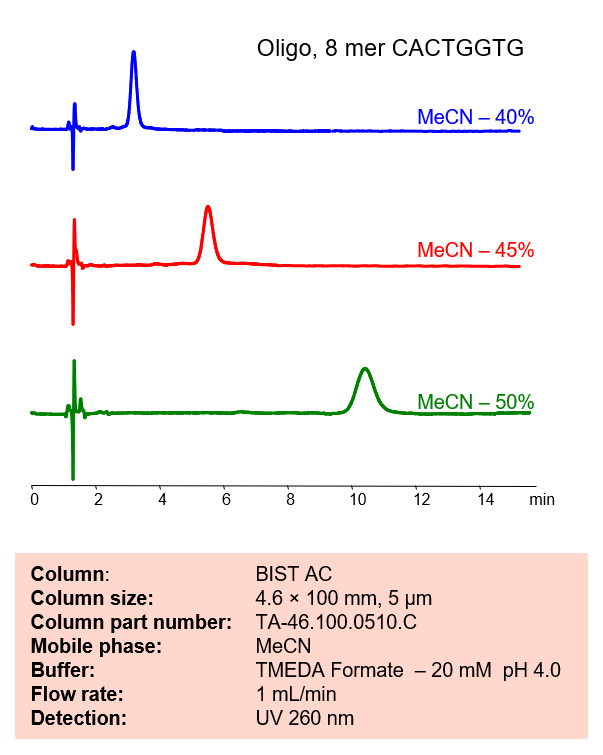
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Oligonucleotides
An oligonucleotide octomer is a short DNA molecule that consists of eight nucleotides. These types of oligonucleotides are commonly used in molecular biology research for various applications, such as PCR, DNA sequencing, gene expression analysis, and gene editing.
Octomer oligonucleotides can be designed to be complementary to a specific DNA sequence of interest and can serve as primers or probes for amplification, detection, or modification of that sequence. For example, in PCR, two octomer oligonucleotides can be used as forward and reverse primers to amplify a target DNA fragment between them.
Octomer oligonucleotides can also be used as building blocks for the synthesis of longer oligonucleotides or genes through enzymatic or chemical methods. Additionally, they can be used as substrates for various DNA-modifying enzymes, such as ligases, kinases, or nucleases.
Overall, octomer oligonucleotides are valuable tools in molecular biology research, allowing scientists to study DNA sequences and manipulate them for various applications. The properties and potential applications of an octomer oligonucleotide will depend on its specific sequence and the experimental conditions used.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, this oligonucleotide can be retained on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as TMEDA formate, which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively charged dye to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, oligonucleotide can be separated, retained, and detected at 260 nm.
Please read more on oligonucleotides analysis by HPLC in our April’s 2023 newsletter.
The sequence consists of the following nucleotides:
C – cytosine A – adenine C – cytosine T – thymine G – guanine G – guanine T – thymine G – guanine
Condition
| Column | BIST AC, 4.6 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | TMEDA formate pH 4.0 – 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
Application Column
BIST AC
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





