Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Oligonucleotides on BIST A Column by SIELC Technologies
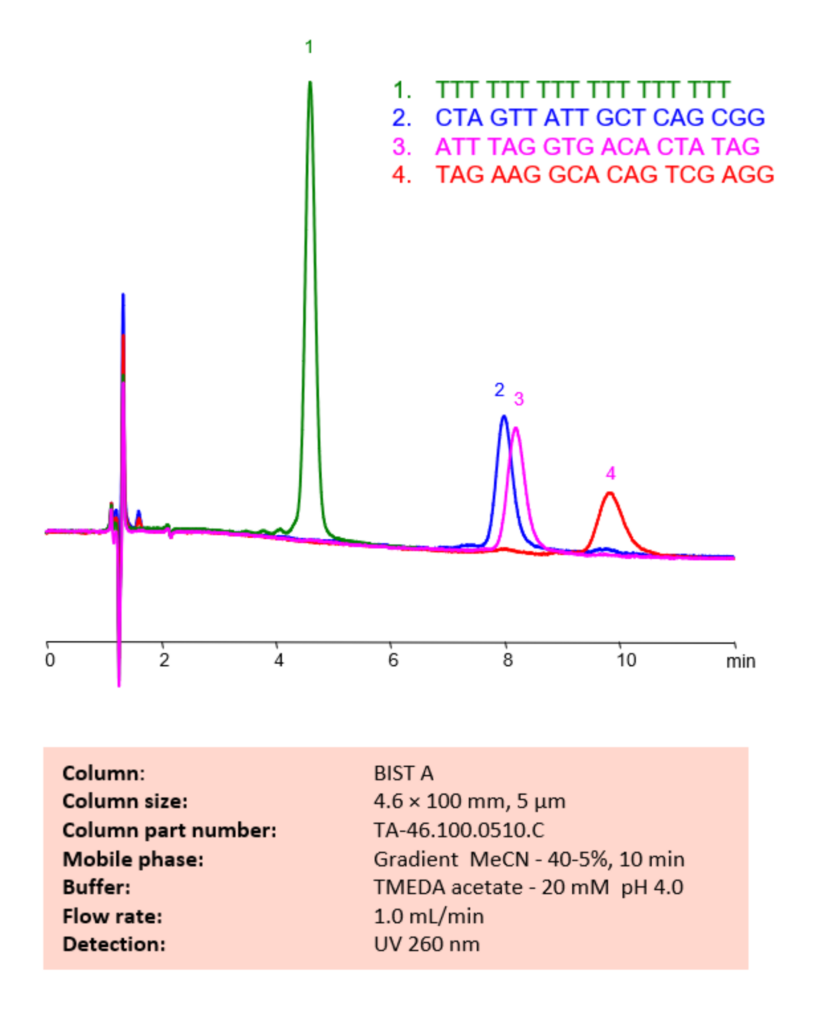
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Oligonucleotides
An 18-mer oligonucleotide is a short DNA molecule that is 18 nucleotides in length. Oligonucleotides of this length are commonly used in molecular biology research for a variety of applications, including PCR, DNA sequencing, gene expression analysis, and gene editing.
One common use of 18-mer oligonucleotides is as primers in PCR. PCR amplifies specific DNA sequences by using oligonucleotide primers that are complementary to the target sequence. The primers hybridize to the template DNA and serve as starting points for DNA polymerase to extend the DNA sequence in the direction of the primer.
In addition to PCR, 18-mer oligonucleotides can also be used as probes for hybridization-based assays such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) or Southern blotting. These assays use oligonucleotide probes that are complementary to a specific DNA sequence of interest to identify the presence or absence of the target sequence.
Furthermore, 18-mer oligonucleotides are often used in gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9. In this technique, an 18-mer oligonucleotide serves as a guide RNA (gRNA) to direct the Cas9 nuclease to the target DNA sequence, where it can make a precise cut and initiate DNA repair processes.
Overall, 18-mer oligonucleotides are versatile tools in molecular biology research that allow scientists to target specific DNA sequences for amplification, detection, and modification.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, this oligonucleotide can be retained on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as TMEDA acetate, which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively charged dye to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, oligonucleotide can be separated, retained, and detected at 260 nm.
Please read more on oligonucleotides analysis by HPLC in our April’s 2023 newsletter.
Condition
| Column | BIST A, 4.6 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, surface coated |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | TMEDA acetate pH 4.0 – 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
Application Column
BIST A
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: surface coated





