Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of 23-mer Oligonucleotides on OligoMg Column by SIELC Technologies
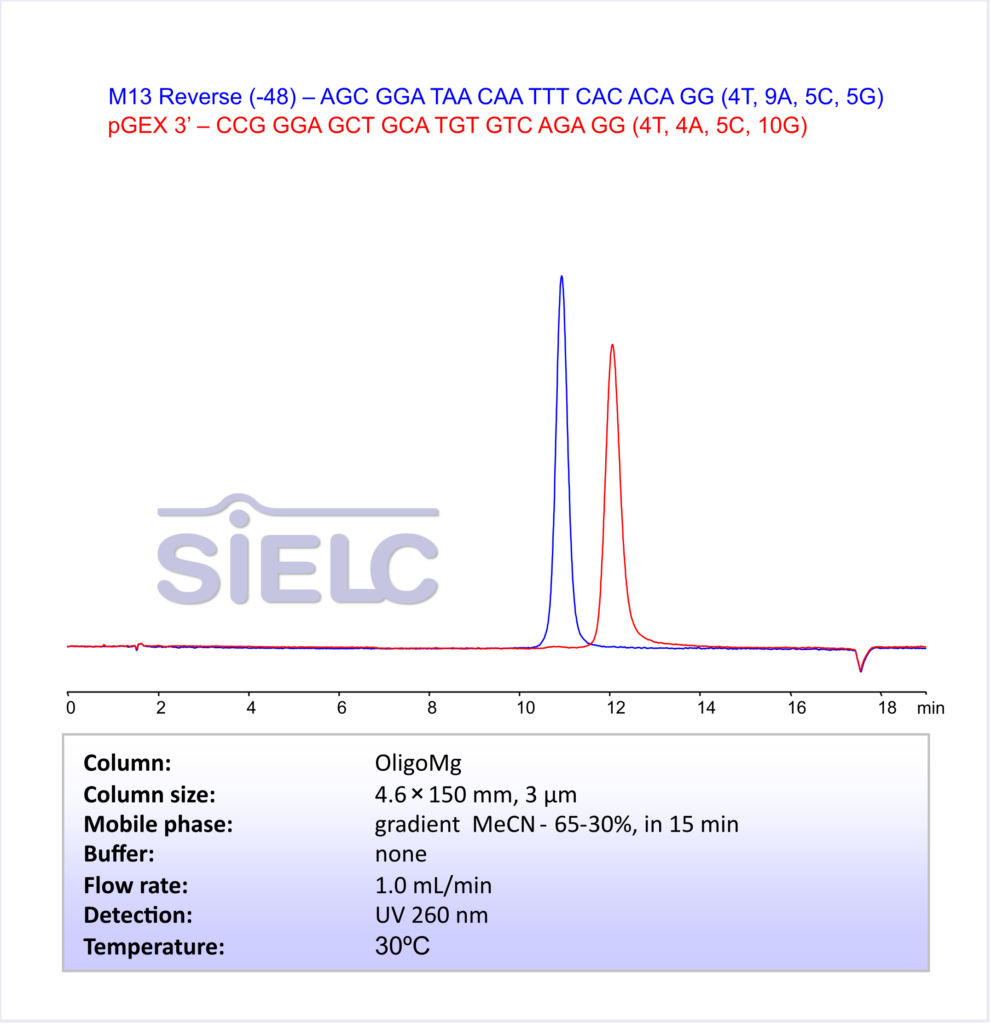
HPLC Method for Analysis of 23-mer Oligonucleotides
23-mer oligonucleotides are short sequences of nucleotides consisting of 23 nucleotide units. These sequences can be composed of any combination of the four standard nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
Research and Studies:
- Molecular Biology: In molecular biology, such oligos can be used as primers for PCR, sequencing, or as probes in hybridization experiments.
- Binding Studies: The poly(A) sequence may be used to study binding interactions with proteins, such as DNA-binding proteins or enzymes.
Medical and Diagnostic Applications:
- As part of diagnostic kits, especially in assays that require hybridization to a complementary sequence.
Educational Purposes:
Demonstrating basic principles of nucleic acid chemistry and genetics.
Nanotechnology:
In DNA nanotechnology, specific sequences of DNA are used to form structures and shapes at the nanoscale. A poly(A) sequence might be part of a larger structure.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, this oligonucleotide can be retained on a OligoMg column. Using this new and unique analysis method, oligonucleotide can be separated, retained, and detected at 260 nm.
Please read more on oligonucleotides analysis by HPLC in our June 2024 newsletter.
Condition
| Column | OligoMg, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN 65-30%, 15 min |
| Buffer | none |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
Application Column
OligoMg
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended