Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™
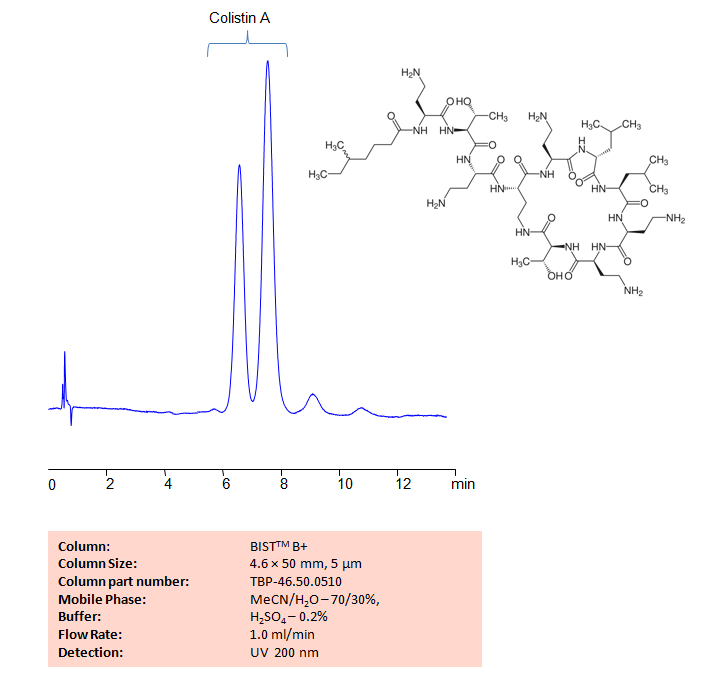
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Colistin A
Colistin A is a last-resort antibiotic drug sued to treat Gram-negative bacterial infection, such as pneumonia. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, Colistin A can be retained on a positively-charged anion-exchange BIST™ B+ column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, negative buffer, such as Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which acts as a bridge, linking the positively-charged Copper and peptide to the positively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, Colistin A can be separated, retained, and UV detected at 200 nm
Condition
| Column | BIST™ B+, 4.6×50 mm, 5µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 70% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Drugs, Antibiotic |
| Analyzing Compounds | Colistin A |
Application Column
BIST B+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select options




