| Synonyms |
|---|
Applications:
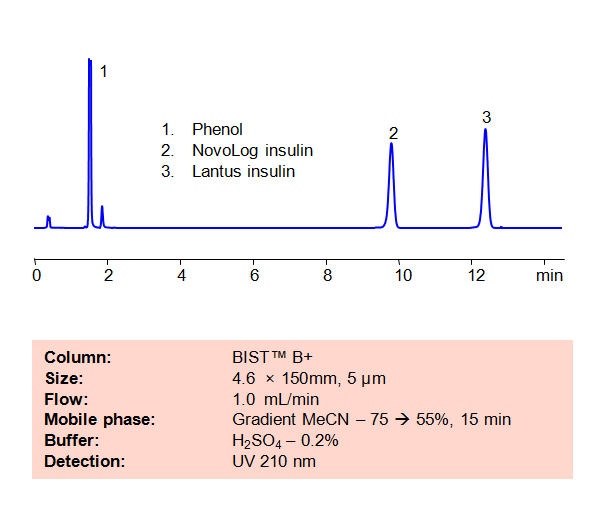
HPLC Method for Analysis of Insulin on BIST™B+ Column
July 8, 2022
| Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ | ||||||||||||||
| High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Insulin.
Insulin is an anabolic peptide hormone naturally produced in the pancreas that regulates the body’s glucose levels. It is also synthesized as a treatment drug for those with Diabetes who can’t regulate their own blood sugar levels naturally. Two well-known forms of synthetic insulin are NovoLog and Lantus. NovoLog is a fast-acting version of insulin and can be used by both Type-1 and Type-2 Diabetes patients, whereas Lantus is a long-acting version of insulin that is primarily used by Type-2 Diabetes patients (and by Type-1 patients under the age of 6). Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™method, these two forms of insulin can be separated and retained on a positively-charged anion-exchange BIST™B column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, negative buffer, such as Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which acts as a bridge, linking the positively-charged amine analytes to the positively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. This method actually utilizes a gradient that lowers the MeCN concentration over time; this reduces the retention effects on the insulin analytes, allowing for quicker elution times while still maintaining clear selectivity and separation. Using this new and unique analysis method, two different manu can be retained and UV detected at 210 nm. |
||||||||||||||
|
Application Column
BIST B+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select optionsInsulin, neutral

HPLC Separation of Human and Synthetic Insulins on Promix Column
May 6, 2011
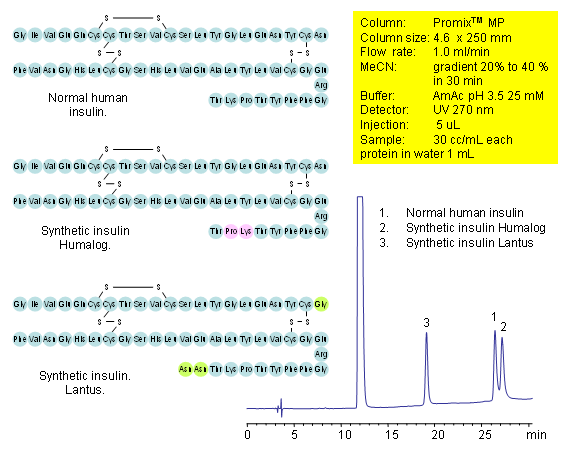
Insulin is a protein that regulates carbohydrates and fat metabolism. Insulin is a peptide hormone consisting of 51 amino acids and has molecular weight of 5808 Da. Bovine insulin differs from human in only three amino acid residues, and porcine insulin in one. Difference in structures is very minimal and the insulin cannot be resolve on reversed-phase column. Mixed-mode approach allows to use small difference in hydrophobic and ionic properties and separate insulins with close structures. Normal human insulin, synthetic insulin Humalog, and synthetic insulin Lantus are separated on a Promix MP mixed-mode HPLC column with LC/MS-compatible conditions. Method does not require use of ion-pairing reagent. Method is also compatible with preparative chromatography and can be used for isolation of insulin on a large scale.
Application Column
Promix MP
The Promix family of mixed-mode columns presents an innovative chromatography technology for the efficient resolution of peptides and proteins. This technology hinges on a unique blend of hydrophobic and ionic interactions, facilitated by a novel separation medium: a ligand bonded to a silica support, chemically combined with hydrophobic and ionic functional groups. This phase provides unparalleled selectivity and peak capacity. By independently adjusting the quantities of buffer and organic modifier, a virtually infinite number of separation conditions can be achieved, rendering it suitable for a wide array of biomolecules.
Select optionsInsulin
Lantus