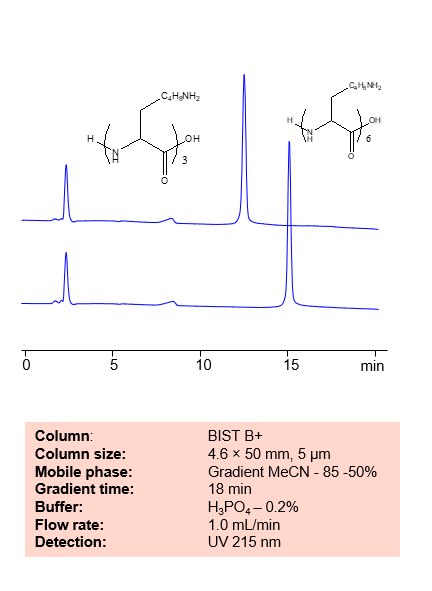
Polylysine includes a large group of similar polymers with various uses. Some are used as food preservatives, while others are used for drug delivery in pharmaceuticals. Polymers with charged monomeric units, such as polylysine, are often difficult to separate using typical ion-exchange chromatography due to very strong and often irreversible interactions with the oppositely charged column surface. Therefore, an extremely high concentration of the buffer, up to several molar, is usually needed to facilitate an ion-exchange process. This high buffer concentration, however, is not desirable because of the significantly increased viscosity of the mobile phase and the salt formation in the pump components. With BIST™, these polymers can be separated and retained with relatively weak buffers (in the mM regime) and a fairly simple gradient. Using this new and unique analysis method, polylysine can be retained and UV detected at 215 nm.
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | H3PO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 215 nm |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements |
| Analyzing Compounds | Lysine-based Peptide Oligomers |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Polylysine
UV Detection