| CAS Number | 89-00-9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H5NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 167.12 |
| InChI Key | GJAWHXHKYYXBSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 0.2 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
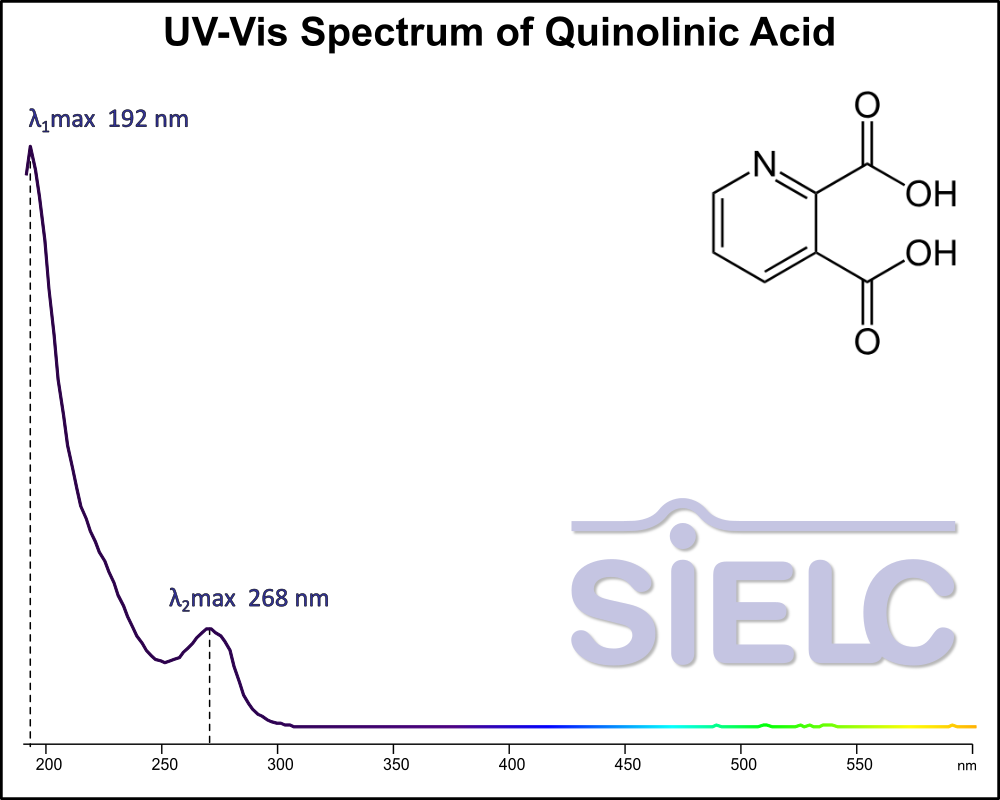
UV-Vis Spectrum of Quinolinic acid
January 5, 2026
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Quinolinic acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

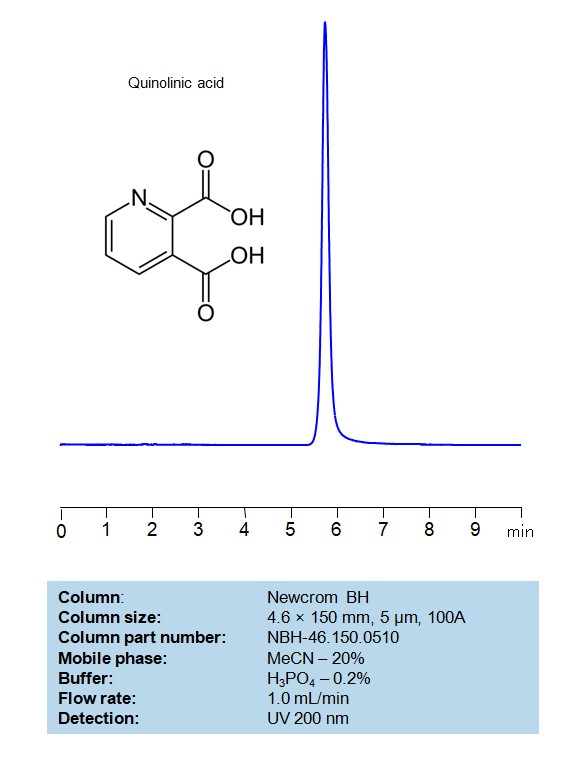
HPLC Method for Analysis of Quinolinic acid on Newcrom BH Column
October 4, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Quinolinic acid on Newcrom BH Column by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Quinolinic acid (also known as quinolinate or 2,3-pyridinedicarboxylic acid) is a dicarboxylic acid with a pyridine backbone. It plays a role in various biological processes and is associated with some pathological conditions.
Biochemical Role:
- Quinolinic acid is a metabolite in the kynurenine pathway, which is responsible for the catabolism of tryptophan, an essential amino acid.
- It serves as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), an essential coenzyme in cellular redox reactions.
Neurological Significance:
- Quinolinic acid can act as an excitotoxin in the brain, meaning it can overactivate nerve cells potentially leading to damage or death of the cells.
- High levels of quinolinic acid have been associated with various neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and others, due to its ability to overstimulate neurons through the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.
Chemical Properties:
- Quinolinic acid has a somewhat polar character due to the carboxylic acid groups and the nitrogen in the pyridine ring.
- It is a weak acid and can lose protons from the carboxylic acid groups, forming salts in neutral and basic conditions.
Environmental Presence:
- Quinolinic acid, like other biologically active molecules, may be found in various environmental contexts, like in soil and water, through natural processes or as a result of anthropogenic activities, such as the use of pesticides that may contain pyridine derivatives.
Quinolinic acid can be retained and analyzed on a mixed-mode Newcrom BH column with a mobile phase consisting of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and posphoric acid. This analytical method can detect compounds with high resolution and peak symmetry using UV detection at 200 nm
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Quinolinic acid
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 20% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Peak Retention Time | 5.38 min |
| Detection | 200 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Quinolinic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended


