| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 131.13 |
| InChI Key | PMMYEEVYMWASQN-DMTCNVIQSA-N |
| LogP | -3.3 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
Uv-Vis Spectrum of Hydroxyproline
January 9, 2026
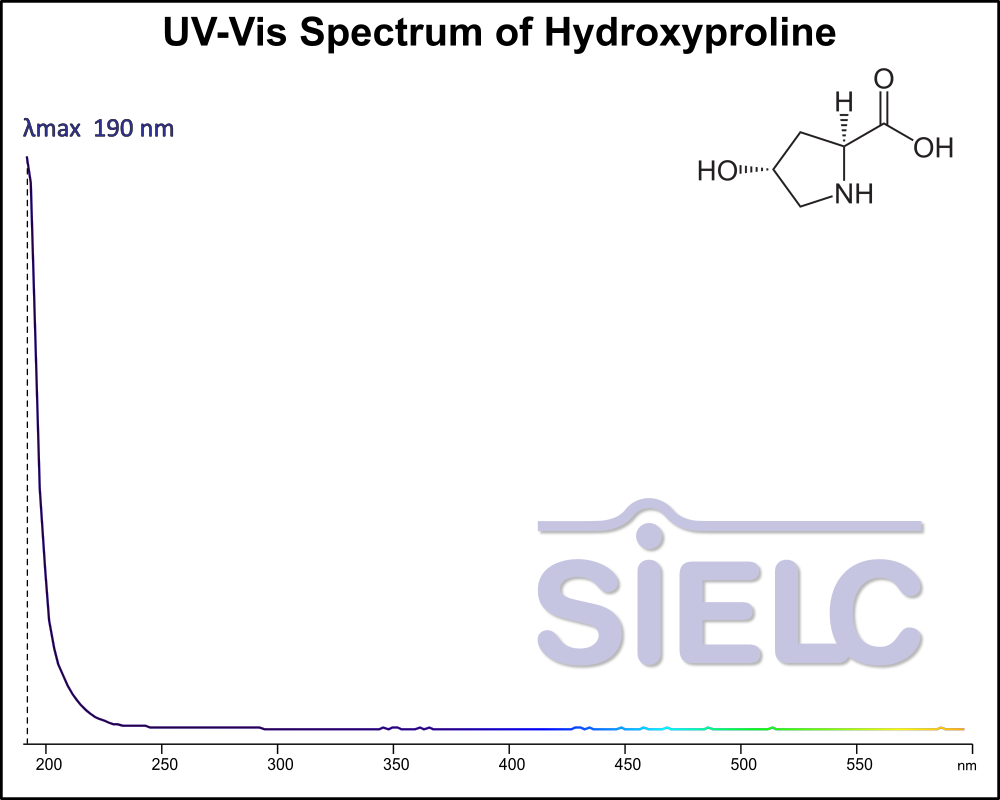
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Hydroxyproline check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

HPLC-MS Method for Analysis of Hydroxyproline, Creatine, and Creatinine on Newcrom AH Column
March 6, 2025
HPLC Method for Analysis of Hydroxyproline, Creatine, Creatinine on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
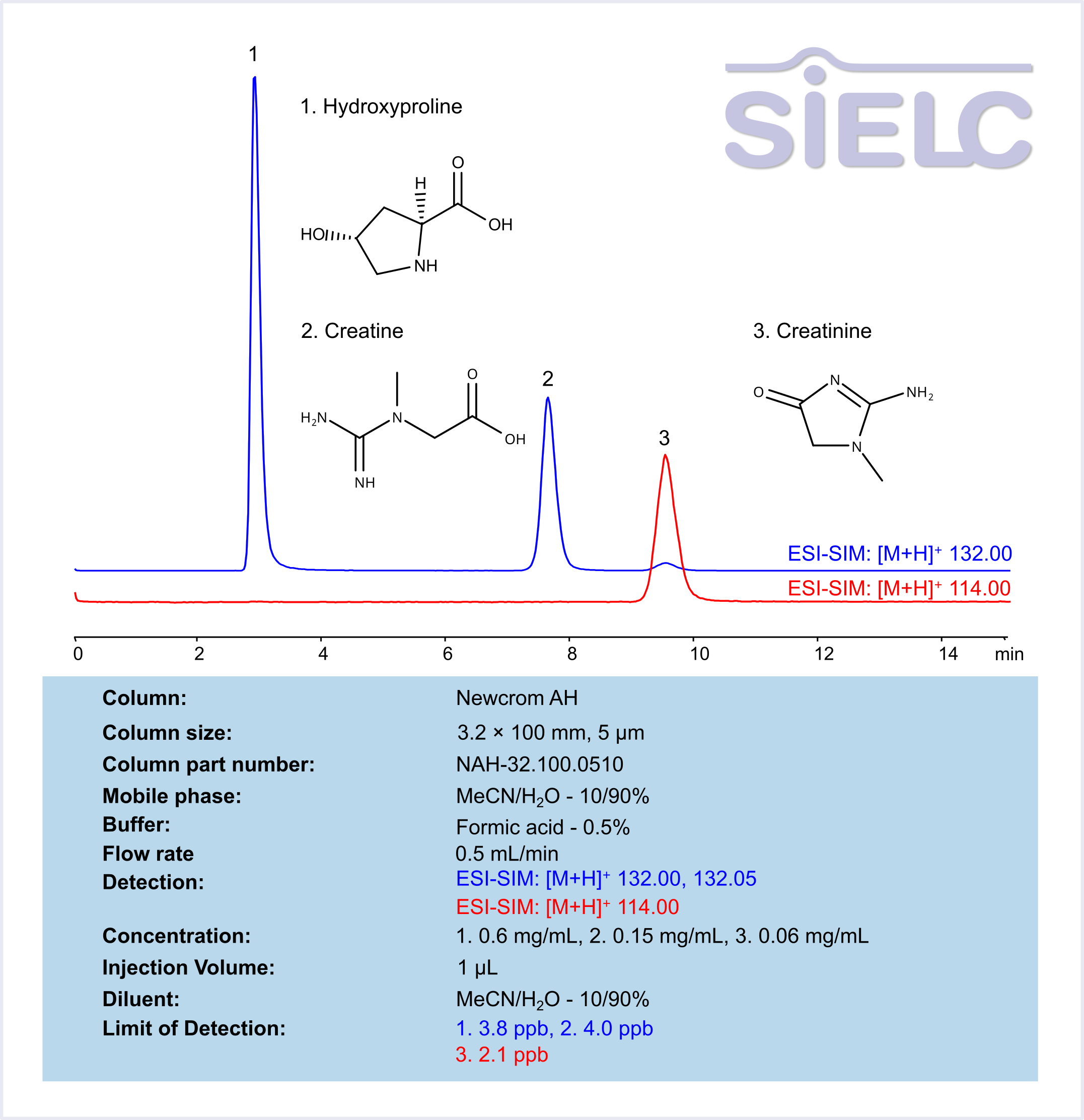
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Hydroxyproline, Creatine, Creatinine
Hydroxyproline is a non-essential amino acid primarily found in collagen, the main structural protein in connective tissues such as skin, bones, and cartilage. It plays a crucial role in maintaining collagen stability and is often used as a biomarker for collagen turnover and connective tissue disorders. Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in muscles and is used to produce energy during high-intensity exercise. It is synthesized in the body from amino acids and stored in muscles for quick energy release. Creatinine, on the other hand, is a waste product produced from the breakdown of creatine. It is filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine. The measurement of creatinine levels in the blood and urine is commonly used to assess kidney function, as high levels may indicate impaired kidney function or other health issues.
Hydroxyproline, Creatine, and Creatinine can be analyzed and separated using a Newcrom AH mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and formic acid as a buffer. Mass spectrometric detection was carried out in ESI-SIM mode, monitoring the ions [M+H]⁺ at m/z 132.00, 132.05, 114.00.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 3.2 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | Formic Acid – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | ESI-SIM: [M+H]⁺ 132.00, 132.05, 114.00 |
| Sample | 1. 0.6 mg/mL, 2. 0.15 mg/mL, 3. 0.06 mg/mL |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 1. 3.8 ppb, 2. 4.0 ppb, 3. 2.1 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Amino Acid-Derived compounds |
| Analyzing Compounds | Hydroxyproline, Creatine, Creatinine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Creatinine
Hydroxyproline

HPLC Method for Analysis of Hydroxyproline, Creatine, and Creatinine on Newcrom AH Column
March 5, 2025
HPLC Method for Analysis of Hydroxyproline, Creatine, Creatinine on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
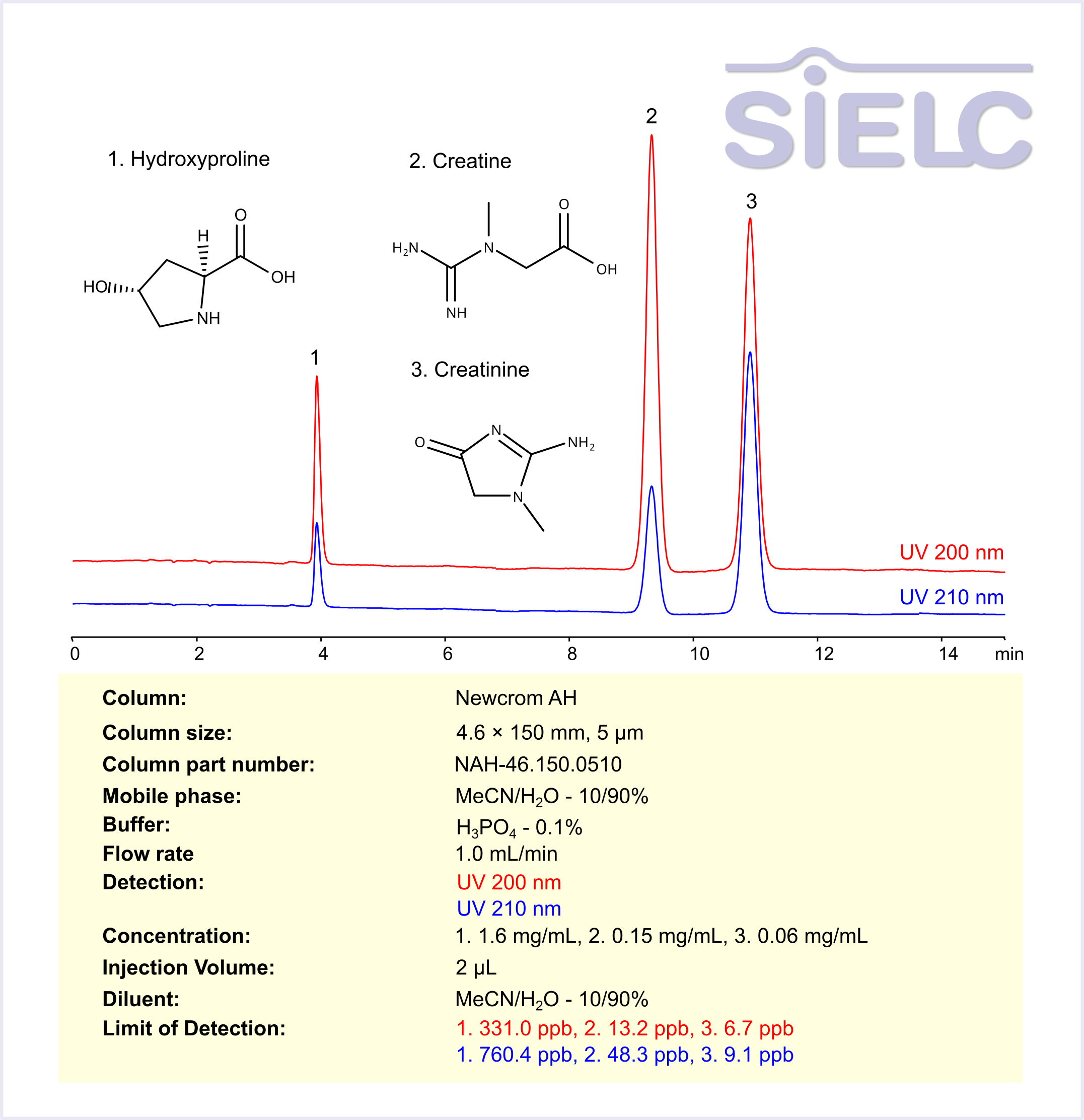
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Hydroxyproline, Creatine, Creatinine
Hydroxyproline is a non-essential amino acid primarily found in collagen, the main structural protein in connective tissues such as skin, bones, and cartilage. It plays a crucial role in maintaining collagen stability and is often used as a biomarker for collagen turnover and connective tissue disorders. Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in muscles and is used to produce energy during high-intensity exercise. It is synthesized in the body from amino acids and stored in muscles for quick energy release. Creatinine, on the other hand, is a waste product produced from the breakdown of creatine. It is filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine. The measurement of creatinine levels in the blood and urine is commonly used to assess kidney function, as high levels may indicate impaired kidney function or other health issues.
Hydroxyproline, Creatine, and Creatinine can be analyzed and separated using a Newcrom AH mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and phosphoric acid as a buffer. Detection is carried out using UV.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm, 210 nm |
| Sample | 1. 1.6 mg/mL, 2. 0.15 mg/mL, 3. 0.06 mg/mL |
| Injection volume | 2 µl |
| LOD* | 1. 331.0 ppb, 2. 13.2 ppb, 3. 6.7 ppb (UV 200 nm) 1. 760.4 ppb, 2. 48.3 ppb, 3. 9.1 ppb (UV 210 nm) |
| Class of Compounds | Amino Acid-Derived compounds |
| Analyzing Compounds | Hydroxyproline, Creatine, Creatinine |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Creatinine
Hydroxyproline

New HPLC Amino Acids Separation Compatible With Carbon Dating Technique
February 11, 2020
HPLC Method for Proline, Glycine, D-Alanine, Alanine, Hydroxyproline on Newcrom AH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Proline, Glycine, D-Alanine, Alanine, Hydroxyproline.
Hydroxyproline seems to be the most promising amino acid used in carbon dating when isolated from bone collagen. Separation of amino acids is challenging, especially without the use of ions or inorganic buffers that can interfere with Mass spectrometer (MS) or contaminate the sample with modern carbon. Amino acids are also not retained in reverse-phase chromatography. The ideal solution would be using water only to separate the amino acids. This would allow a direct coupling to MS. We were able to separate hydroxyproline from proline and other simple amino acids like glycine and alanine in HPLC on Newcrom AH column using water only as a mobile phase. Using water also allowed UV detection at 205 nm which can’t be done if using a buffer based on acetic or formic acid.
See more information on radiocarbon dating here.
The same method can be modified to get symmetrical peaks and higher efficiency if a mobile phase with ionic modifier such as formic acid is used.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Proline and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
You can find detailed UV spectra of Glycine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
| Column | Newcrom AH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 205 nm, CAD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Proline, Glycine, D-Alanine, Alanine, Hydroxyproline |
Application Column
Newcrom AH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
D-Alanine
Glycine
Hydroxyproline
Proline
CAD Detection




