HPLC Method for Analysis of Chlorhexidine in Biofluids: Blood Plasma and Urine on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
Chlorhexidine is a common antiseptic used intensively in hand sanitizers and other antibacterial products. It has the chemical formula C22H30Cl2N10. It is primarily used for skin surgical instrument disinfection. Despite being used in mouthwash, one of the most common side effects is tooth discoloration. You can find detailed UV spectra of Chlorhexidine and information about its various lambda maxima by visiting the following link.
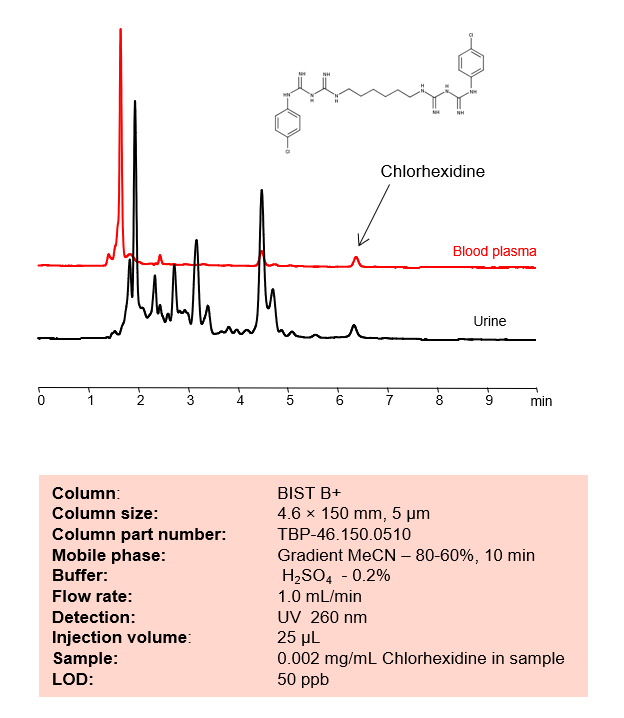
Typical HPLC methods used to analyze this product are done in reverse phase (RP) mode, but this is complicated by the presence of two basic groups which, with the overall hydrophobic characteristics of the molecule, usually produce asymmetrical peaks.
Chlorhexidine can be retained and analyzed using the BIST B+ stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a sulfuric acid buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 6.2 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Topical antiseptic |
| Analyzing Compounds | Chlorhexidine |
Sample preparation:
| Plasma/urine sample was spiked with a small amount of Chlorhexidine and then diluted 5 times with acetonitrile. A formed precipitate was removed by centrifugation and the cleared solution was used directly for injection. |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





