HPLC Method for Analysis of Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) on BIST B+ by SIELC Technologies.
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
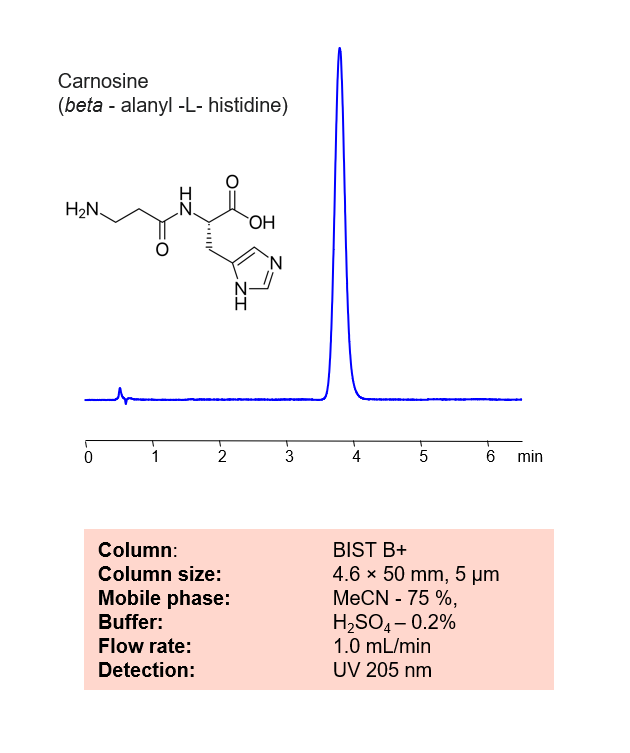
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine)
Carnosine is a dipeptide molecule synthesized from beta-alanine and histidine. It is a naturally occurring pH buffer with antioxidant properties found in muscles. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, Carnosine can be retained on a positively charged, antion-exchange BIST™ B+ column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, negative buffer, such as Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which acts as a bridge, linking the positively charged peptide to the positively charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, Carnosine can be separated, retained, and UV detected at 205 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST B+, 4.6×50 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 75% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 205 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 3.71 min |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Dipeptide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) |
Application Column
BIST B+
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





