Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of DNA Oligo, 5 bases (AAAAA) on BIST A Column by SIELC Technologies
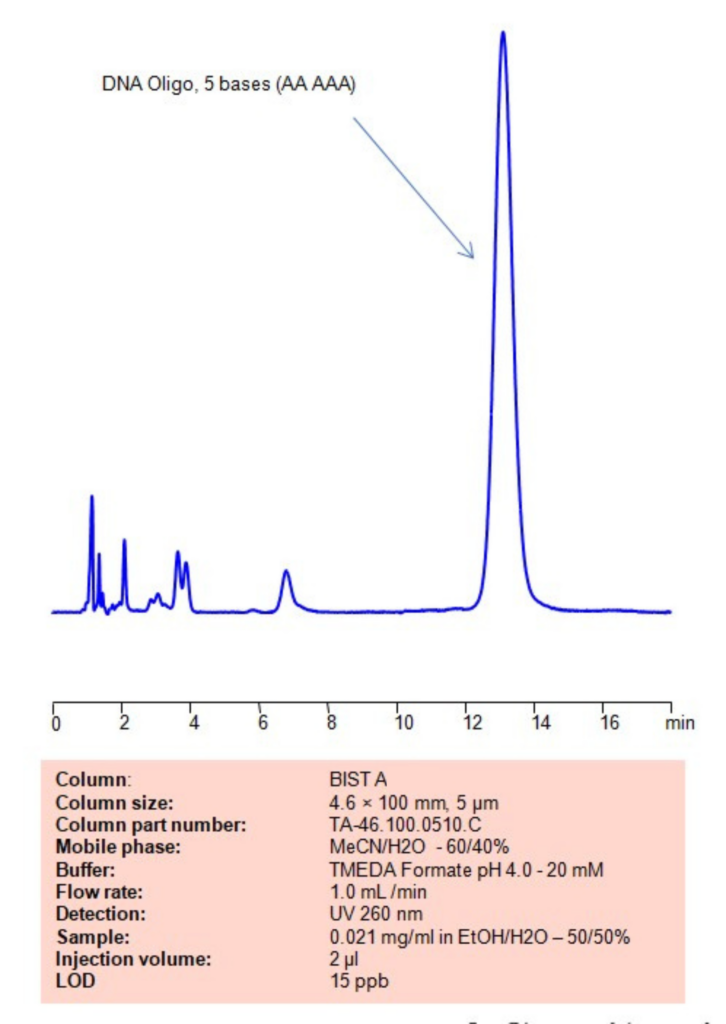
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of DNA Oligo, 5 bases (AAAAA)
Synthesis of DNA Oligonucleotide (AAAAA)
- Automated Synthesis:
- DNA oligonucleotides, including a sequence like “AAAAA”, are typically synthesized using automated synthesizers based on solid-phase synthesis.
- The process involves the sequential addition of nucleotide residues to the growing chain in a step-wise manner, starting from the 3′-end of the oligo.
- Chemistry:
- The synthesis uses phosphoramidite chemistry, where each nucleotide to be added is in its protected phosphoramidite form.
- The process includes coupling, capping, oxidation, and deprotection steps.
- Purification:
- After synthesis, the oligonucleotide is usually cleaved from the solid support and deprotected.
- It is then purified, commonly by methods like HPLC or PAGE (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis), depending on the required purity level.
Using DNA Oligo (AAAAA)
The application of a DNA oligo with a sequence “AAAAA” can vary based on the context:
- Research and Studies:
- Molecular Biology: In molecular biology, such oligos can be used as primers for PCR, sequencing, or as probes in hybridization experiments.
- Binding Studies: The poly(A) sequence may be used to study binding interactions with proteins, such as DNA-binding proteins or enzymes.
- Medical and Diagnostic Applications:
- As part of diagnostic kits, especially in assays that require hybridization to a complementary sequence.
- Educational Purposes:
- Demonstrating basic principles of nucleic acid chemistry and genetics.
- Nanotechnology:
- In DNA nanotechnology, specific sequences of DNA are used to form structures and shapes at the nanoscale. A poly(A) sequence might be part of a larger structure.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, this oligonucleotide can be retained on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as TMEDA formate, which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively charged dye to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, oligonucleotide can be separated, retained, and detected at 260 nm.
Condition
| Column | BIST A, 4.6 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, surface coated |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 60% |
| Buffer | TMEDA Formate pH 4.0 – 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 260 nm |
| Sample | 0.021 mg/ml in EtOH/H2O – 50/50% |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 15 ppb |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Oligonucleotides |
Application Column
BIST A
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: surface coated





