HPLC Method for Analysis of Acetylcholine on Obelisc R by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter, which is a chemical messenger that transmits signals across synapses, the gaps between nerve cells or between nerve cells and muscles. It plays a crucial role in the nervous system, both in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Here are key points about acetylcholine:
- Chemical Structure: Acetylcholine is derived from the combination of choline and acetyl coenzyme A. Its chemical formula is (CH_3COOCH_2CH_2N(CH_3)_3^+).
- Synthesis and Release: Acetylcholine is synthesized within nerve cells through a series of enzymatic reactions. Upon a nerve impulse reaching the end of a nerve cell, acetylcholine is released into the synapse.
- Neuromuscular Junction: In the peripheral nervous system, acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals from motor neurons to muscle fibers at the neuromuscular junction. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors on the muscle cell membrane triggers muscle contraction.
- Autonomic Nervous System: In the autonomic nervous system, acetylcholine is involved in transmitting signals in the parasympathetic branch. It slows the heart rate, stimulates digestive processes, and promotes a “rest and digest” response.
- Cognitive Functions: In the central nervous system, acetylcholine is implicated in various cognitive functions, including memory, learning, and attention. Its role in the brain is complex and involves interactions with different receptor types.
- Degradation: The enzyme acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft, terminating its action and preventing continuous stimulation.
- Medicinal Importance: Drugs that affect acetylcholine receptors or inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity are used for various medical purposes. For example, some medications aim to enhance acetylcholine activity in Alzheimer’s disease.
The balance of acetylcholine and other neurotransmitters is essential for proper nervous system function. Imbalances in acetylcholine levels have been implicated in various neurological disorders.
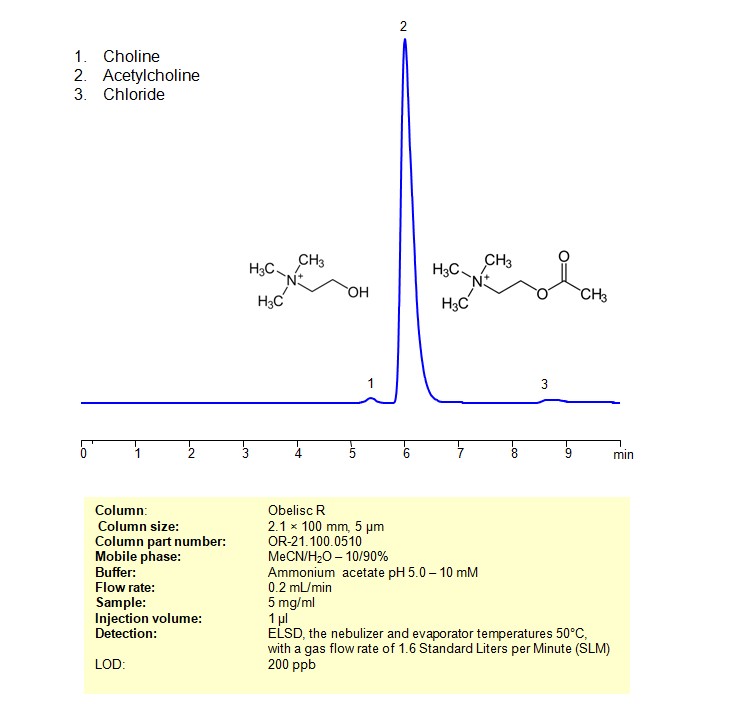
Acetylcholine can be retained and analyzed using an Obelisc R mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium acetate as a buffer. Detection is achieved using ELSD
| Column | Obelisc R, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | Ammonium acetate pH 5.0 – 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| Samples | 5 mg/ml |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 200 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Quaternity amines |
| Analyzing Compounds | Acetylcholine |
Application Column
Obelisc R
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





