| CAS Number | 141-83-3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2H6N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 102.098 |
| InChI Key | SQSPRWMERUQXNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -1.28 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
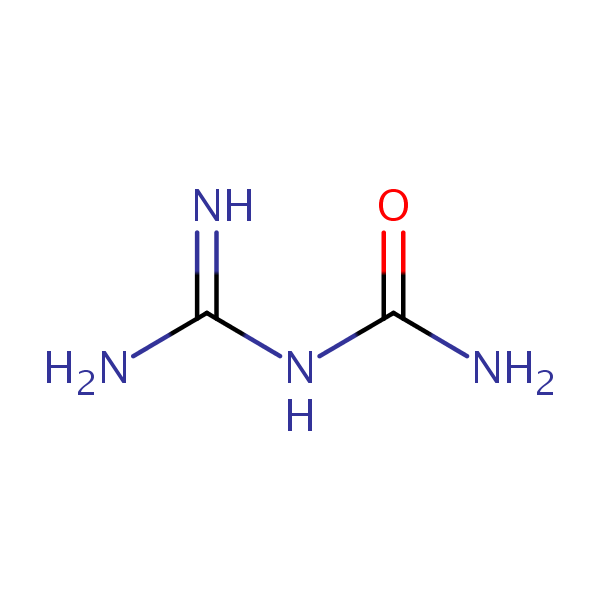
UV-Vis Spectrum of Guanylurea
July 1, 2024
Access the UV-Vis Spectrum SIELC Library
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Guanylurea check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.

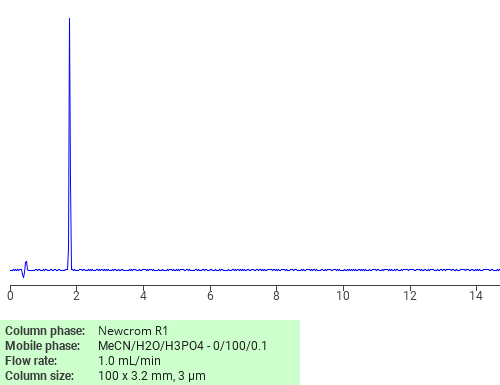
HPLC Method for Separation of 1,2,4-Triazole and Guanylurea on Primesep 100 Column
January 9, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of Guanylurea, 1,2,4-Triazole on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Guanylurea, 1,2,4-Triazole
Guanylurea, also known as guanidylurea, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula (C_3H_7N_5O). It is derived from guanidine and urea, and it has interesting applications in the field of chemistry and materials science.
- Crystal Growth: Guanylurea is known for its use in crystal growth processes. It has been utilized as an additive in solution to control and promote the growth of certain crystals, including organic and inorganic crystals. Guanylurea is part of the broader field of crystal engineering, where researchers explore the design and synthesis of crystalline materials with specific properties. The ability of guanylurea to form hydrogen bonds makes it relevant in this context.
- Hydrogen Bonding Studies: Due to its unique structure, guanylurea has been studied for its hydrogen bonding properties, which are important in various chemical and biological processes.The presence of amino groups in guanylurea allows it to participate in hydrogen bonding interactions, which are crucial in determining the structure and properties of molecular assemblies.
It’s important to note that guanylurea’s applications are primarily in the realm of crystal engineering and related studies. Its ability to participate in hydrogen bonding interactions makes it a valuable component in the design and manipulation of crystalline materials for various purposes.
1,2,4-triazole is a heterocyclic compound with a unique five-membered ring structure. Its versatility, biological activities, and ability to coordinate with metal ions make it a compound of interest in various scientific and medicinal applications.
The 1,2,4-triazole and Guanylurea be retained, separated and analyzed using a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase comprising water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. This method allows for detection using UV at 200 nm
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 10/90% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
| Samples | Guanylurea – 0.77mg/mL 1,2,4-Triazole – 3.9mg/mL |
| Injection volume | 3 µl |
| LOD* | Guanylurea – 5 ppb 1,2,4-Triazole – 25 ppb |
| Class of Compounds | Aromatic amines, Ureas |
| Analyzing Compounds | Guanylurea, 1,2,4-Triazole |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Guanylurea

HPLC Method for Separation of Guanylurea and Metformin on Primesep 100 Column
November 27, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Guanylurea, Metformin on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
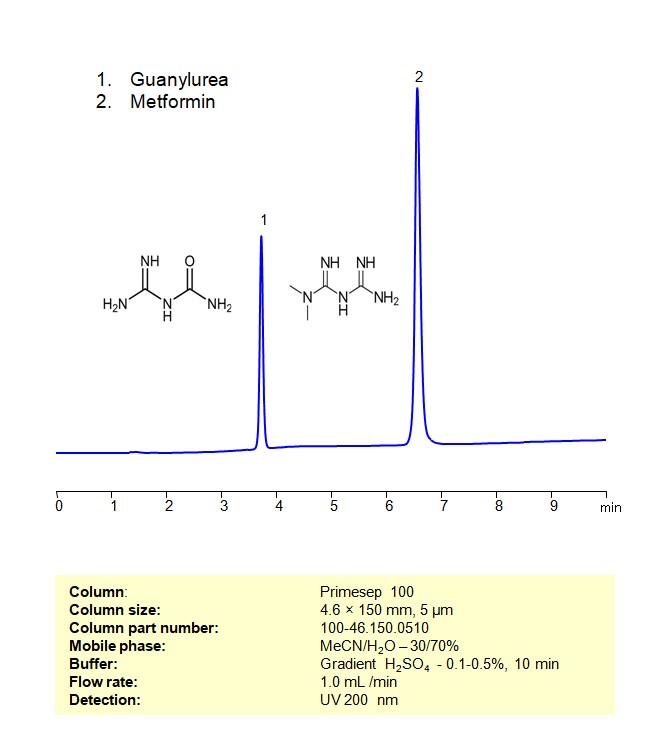
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Guanylurea, Metformin
Guanylurea is a known degradation product of metformin. When metformin undergoes biotransformation in the body, one of the metabolic pathways leads to the formation of guanylurea. This process is a part of the pharmacokinetics of metformin, where the drug is metabolized and eventually excreted from the body.
The conversion of metformin to guanylurea is significant for a few reasons:
Pharmacokinetics: Understanding the metabolism of metformin, including its conversion to guanylurea, is important for comprehending its action in the body, its elimination, and any potential metabolite-related effects.
Environmental Impact: The presence of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites, like guanylurea from metformin, in the environment (especially in water sources) has become a topic of environmental concern. This is because these compounds can have effects on aquatic life and potentially re-enter the human water supply.
Safety and Efficacy: Knowing the metabolites of a drug helps in assessing its safety and efficacy. While guanylurea is not known to have significant pharmacological effects in the context of metformin’s use as a diabetes medication, its identification is essential for a complete understanding of the drug’s profile.
Guanylurea: This is the main known metabolite of metformin. It is formed through the breakdown of metformin in the liver. Despite being the primary metabolite, guanylurea is considered to have minimal pharmacological activity, especially in the context of the glucose-lowering effects of metformin.
Guanylurea and Metformin can be retained, separated and analyzed on a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column using an analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using UV at 200 nm.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 30/70% |
| Buffer | Gradient H2SO4 -0.1-0.5%, 10 min |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
| Sample | Guanylurea phosphate 0.2 mg/ml in H2O and 1,1-Dimethylbiguanide hydrochloride 0.2 mg/ml in H2O |
| Class of Compounds | Ureas |
| Analyzing Compounds | Guanylurea, Metformin |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Metformin

HPLC ELSD Method for Analysis of Guanylurea on Primesep 100 Column
November 22, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Guanylurea on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
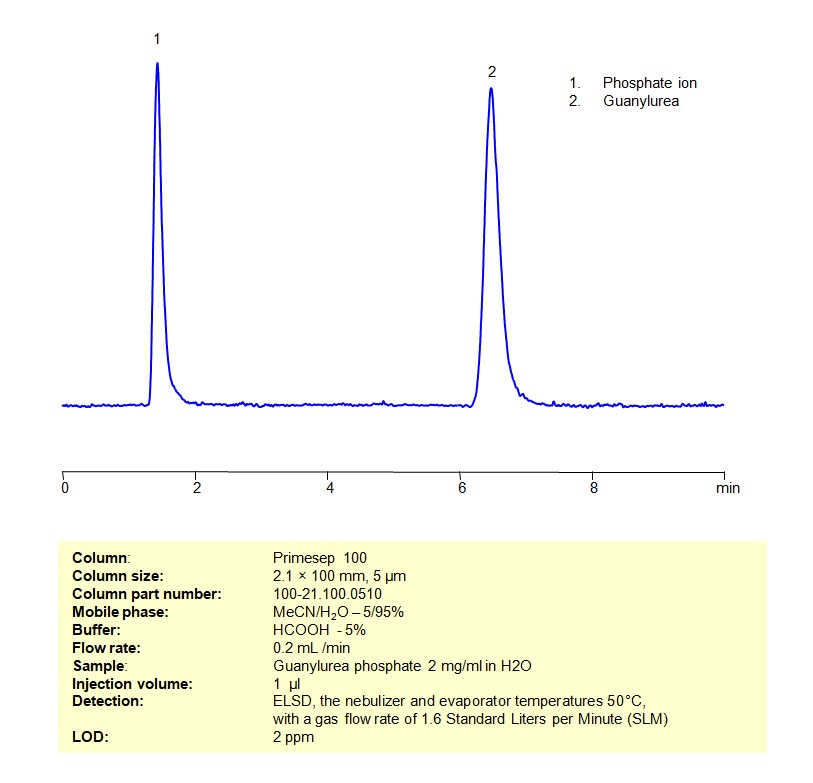
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Guanylurea
Guanylurea, also known as guanylurea phosphate or imidodicarbonimidic diamide, is a chemical compound with the formula C2H6N4O. It is derived from guanidine, a compound found in the urine of mammals, which is itself a derivative of urea.
The structure of guanylurea is characterized by a urea molecule (carbonyl group flanked by two amine groups) connected to an additional amine group. This structure imparts unique chemical properties to guanylurea, making it distinct from simpler urea.
In terms of its applications and uses:
Agriculture: Guanylurea can be used as a source of nitrogen in fertilizers, similar to urea. Its efficacy as a fertilizer comes from its ability to release nitrogen slowly into the soil, which can be beneficial for plant growth.
Chemical Synthesis: It may be used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemical compounds, particularly in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Research: In scientific research, guanylurea may be studied for its chemical properties and potential applications in various fields.
Guanylurea can be retained, and analyzed on a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a formic acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using ELSD.
| Column | Primesep 100, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 5/95% |
| Buffer | Formic acid – 5% |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| Sample | Guanylurea phosphate 2 mg/ml in H2O |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 2 ppm |
*LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed.
| Class of Compounds | Ureas |
| Analyzing Compounds | Guanylurea |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

HPLC Method for Analysis of Guanylurea on Primesep 100 Column
November 22, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Guanylurea on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
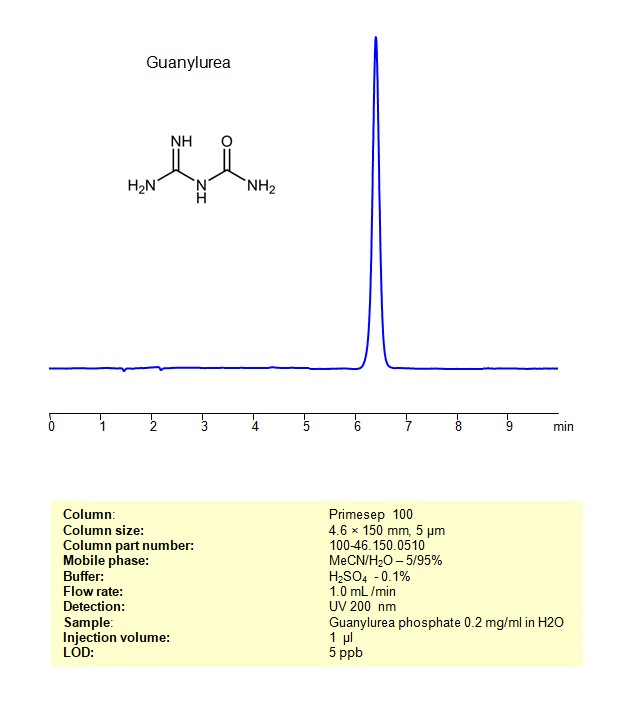
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Guanylurea
Guanylurea, also known as guanylurea phosphate or imidodicarbonimidic diamide, is a chemical compound with the formula C2H6N4O. It is derived from guanidine, a compound found in the urine of mammals, which is itself a derivative of urea.
The structure of guanylurea is characterized by a urea molecule (carbonyl group flanked by two amine groups) connected to an additional amine group. This structure imparts unique chemical properties to guanylurea, making it distinct from simpler urea.
In terms of its applications and uses:
Agriculture: Guanylurea can be used as a source of nitrogen in fertilizers, similar to urea. Its efficacy as a fertilizer comes from its ability to release nitrogen slowly into the soil, which can be beneficial for plant growth.
Chemical Synthesis: It may be used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemical compounds, particularly in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Research: In scientific research, guanylurea may be studied for its chemical properties and potential applications in various fields.
Guanylurea can be retained, and analyzed on a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a sulfuric acid as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using UV at 200 nm.
| Column | Primesep 100, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 5/95% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 -0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
| Sample | Guanylurea phosphate 0.2 mg/ml in H2O |
| Injection volume | 1 µl |
| LOD* | 5 ppb |
*LOD was determined for this combination of instrument, method, and analyte, and it can vary from one laboratory to another even when the same general type of analysis is being performed.
| Class of Compounds | Ureas |
| Analyzing Compounds | Guanylurea |
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

Separation of Guanylurea on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Guanylurea can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options