![Demethoxycurcumin
22608-11-3
24939-17-1
curcumin II
monodemethoxycurcumin
desmethoxycurcumin
BHCFM
4-Hydroxycinnamoyl(feroyl)methane
Demethoxy Curcumin
33171-16-3
(1E,6E)-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
Feruloyl-P-hydroxycinnnamoylmethane
curcuminII
(E/Z)-Demethoxycurcumin
1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione, 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-
p-Hydroxycinnamoylferuloylmethane
UNII-W2F8059T80
CHEBI:65737
4-hydroxycinnamoyl(feruloyl)methane
C20H18O5
NSC687841
(1E,6E)-1-(4-HYDROXY-3-METHOXY-PHENYL)-7-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)HEPTA-1,6-DI ENE-3,5-DIONE
W2F8059T80
1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione
p-Hydroxycinnamoyl-feruloylmethane
demethoxy-curcumin
(1E,6E)-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione
(1E,6E)-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione, 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (1E,6E)-
(2E)-Demethoxy Curcumin
MFCD03427310
Curcumin II;Desmethoxycurcumin;Monodemethoxycurcumin
feruloyl-p-coumaroylmethane
D03EDF
(E,E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione
SCHEMBL431246
CHEMBL105360
INS NO.100(II)
SCHEMBL2553051
DEMETHOXYCURCUMIN [INCI]
SCHEMBL13521973
SCHEMBL23884878
SCHEMBL23884879
cid_5324476
HY-N0006A
INS-100(II)
DTXSID00873751
DESMETHOXYCURCUMIN [USP-RS]
Demethoxycurcumin, >=98% (HPLC)
BDBM50163744
E-100(II)
s9280
Demethoxycurcumin, analytical standard
AKOS015903509
CCG-267896
NSC-687841
AC-34584
BS-48948
CS-0009120
A14545
A910179
6-Bromo-2-pyridin-4-yl-quinoline-4-carboxylicacid
Q-100287
Q5264607
1-(4-Hydroxystyryl)-3-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxystyryl)propanedial
(1E,6E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione, 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)- (VAN)
1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione, 9CI
1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione
5-hydroxy-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one
(1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one
(1E,6E)-1-(4-HYDROXY-3-METHOXY-PHENYL)-7-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)HEPTA-1,6-DIENE-3,5-DIONE](https://sielc.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Demethoxycurcumin.svg_-300x79.png)
| CAS Number | 22608-11-3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H18O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 338.4 |
| InChI Key | HJTVQHVGMGKONQ-LUZURFALSA-N |
| LogP | 3.3 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Demethoxycurcumin
July 25, 2024
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.

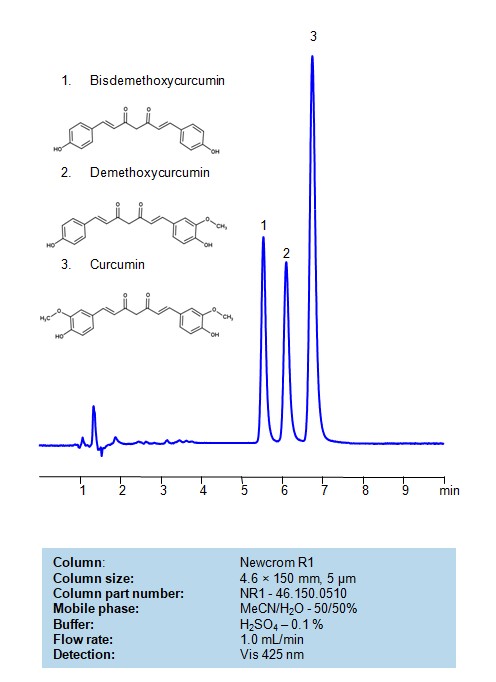
HPLC Method for Analysis of Curcuminoids in Turmeric Capsules on Newcrom R1 Column
September 21, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Curcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin, Demethoxycurcumin on Newcrom R1 Column by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Reversed-phase
Turmeric is a yellow spice derived from the rhizomes of the plant Curcuma longa. It has been used for centuries in culinary and medicinal traditions, especially in Indian and Southeast Asian cultures. One of the main bioactive components responsible for many of turmeric’s potential health benefits is curcumin.
The curcumin content in turmeric varies depending on the source and preparation, but typically, dried turmeric powder contains about 2-5% curcumin by weight. This relatively low percentage is one reason why many curcumin supplements are made using extracts to provide a concentrated dose.
Curcumin is not a single compound but is rather a mixture of related compounds known as curcuminoids.
Curcuminoids are a group of polyphenolic compounds found in turmeric (Curcuma longa). They are responsible for the yellow color of the turmeric spice and are also the main bioactive components believed to be responsible for many of the potential health benefits of turmeric.
The three primary curcuminoids in turmeric are:
Curcumin (diferuloylmethane): This is the primary and most studied component, accounting for 60-70% of the curcuminoids in turmeric.
Demethoxycurcumin: This compound constitutes about 20-27% of the curcuminoids.
Bisdemethoxycurcumin: This makes up around 10-15% of the curcuminoids.
These compounds have been studied for their potential anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and neuroprotective properties, among others. Due to their low bioavailability, many formulations, such as those combined with piperine (from black pepper), have been developed to enhance absorption in the body.
Curcuminoids can be retained, separated, and analyzed on a mixed-mode Newcrom R1 column with a mobile phase consisting of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid. This analytical method can be detected with high resolution and peak symmetry at a wavelength of 425 nm using Vis detection
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Curcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin, Demethoxycurcumin on Newcrom R1 Column by SIELC Technologies
Condition
| Column | Newcrom R1, 0.5 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50%, |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | Vis 425 nm |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Polyphenols |
| Analyzing Compounds | Curcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin, Demethoxycurcumin |
Application Column
Newcrom R1
Column Diameter: 0.5 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Curcumin
Demethoxycurcumin


