| CAS Number | 87-69-4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 150.086 |
| InChI Key | FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N |
| LogP | -1.47 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
UV-Vis Spectrum of Tartaric Acid
December 18, 2025
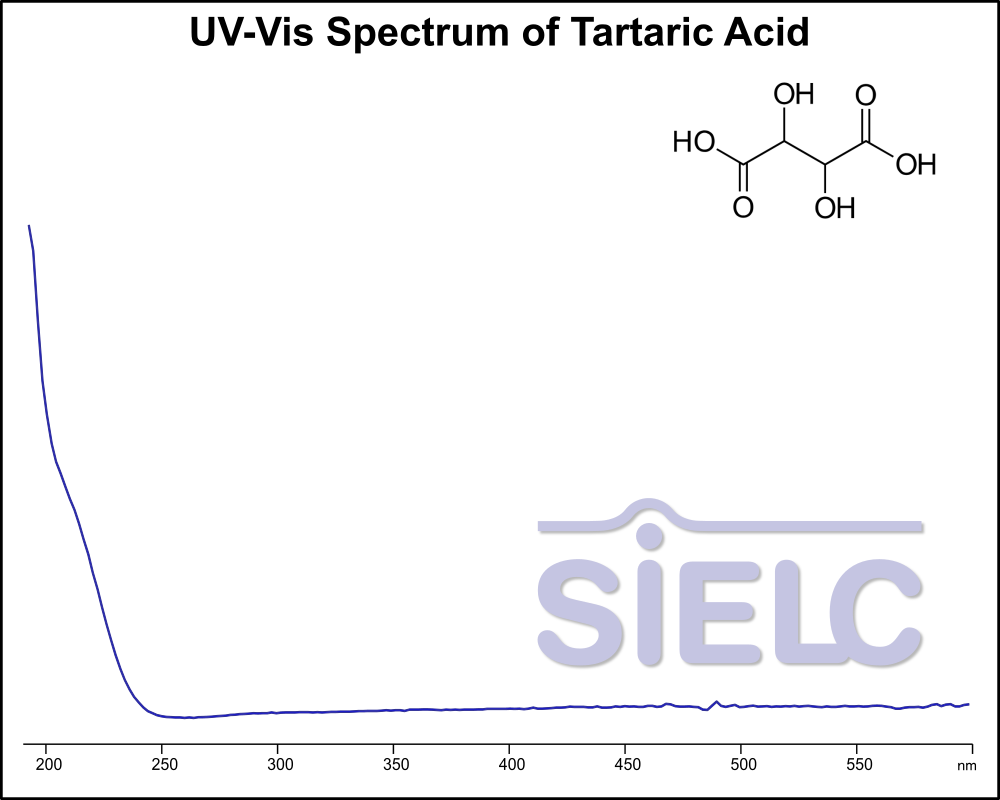
If you are looking for optimized HPLC method to analyze Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid check our HPLC Applications library
For optimal results in HPLC analysis, it is recommended to measure absorbance at a wavelength that matches the absorption maximum of the compound(s) being analyzed. The UV spectrum shown can assist in selecting an appropriate wavelength for your analysis. Please note that certain mobile phases and buffers may block wavelengths below 230 nm, rendering absorbance measurement at these wavelengths ineffective. If detection below 230 nm is required, it is recommended to use acetonitrile and water as low UV-transparent mobile phases, with phosphoric acid and its salts, sulfuric acid, and TFA as buffers.
For some compounds, the UV-Vis Spectrum is affected by the pH of the mobile phase. The spectra presented here are measured with an acidic mobile phase that has a pH of 3 or lower.
dl-Tartaric acid

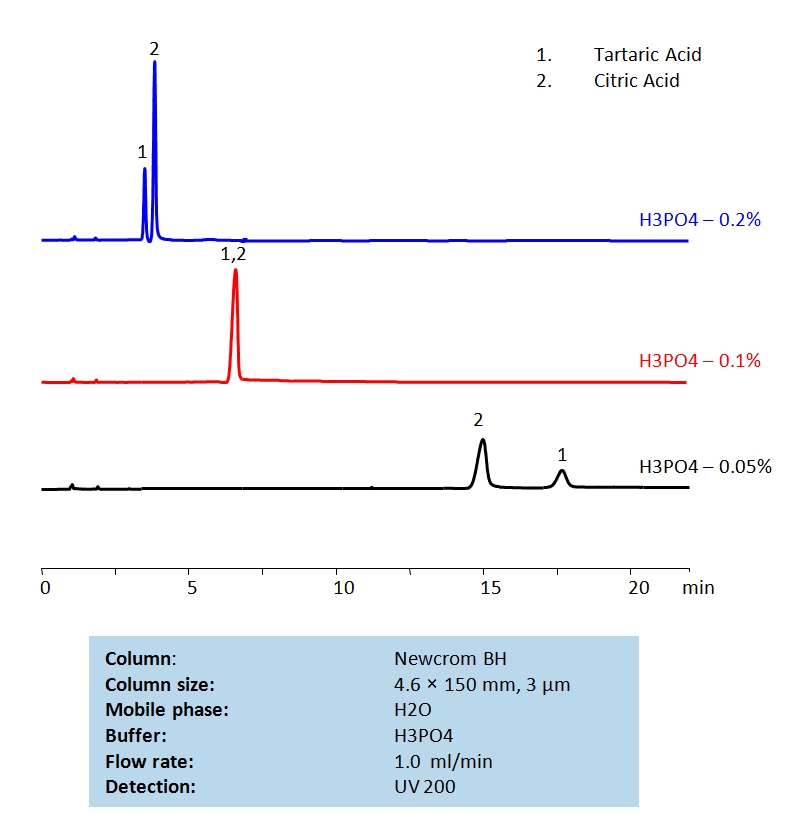
HPLC Separation of Tartaric Acid and Citric Acids on Newcrom BH Column
March 22, 2021
HPLC Method for Citric Acid, Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Citric Acid, Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid.
Tartaric acid is a naturally occurring organic acid that is found in many plants, particularly in grapes and tamarinds. It’s known for its sour taste and antioxidant properties. Chemically, tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid. It has the chemical formula C4H6O6. Tartaric acid has been used in winemaking for centuries because it plays a key role in the fermentation process. It’s also used in baking powder, where it serves as a leavening agent. In addition to these culinary uses, tartaric acid is used in the manufacturing of effervescent salts, in combination with citric acid, to improve taste and make a fizz. It’s also found in some of the very effective rust removal and cleaning solutions. Tartaric acid is used in cream of tartar (potassium bitartrate), which is used in cooking and baking. It can also be found in a variety of other foods, including soft drinks, fruit juices, candies, and ice cream. Like other acids, tartaric acid can be hazardous in large quantities, and it should always be handled and stored appropriately. Always refer to the safety data sheet for this substance and follow the recommended safety guidelines.
Citric Acid is a naturally occurring organic acid found in citrus fruits; it is also an intermediate in the citric acid cycle of aerobic organisms. It is used industrially as an acidity regulator, flavoring, detergent, and more than 2 million tons are produced annually. It’s chemical formula is C₆H₈O₇.
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | H2O |
| Buffer | H3PO4 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Hydrophilic |
| Analyzing Compounds | Citric Acid, Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Tartaric Acid
dl-Tartaric acid

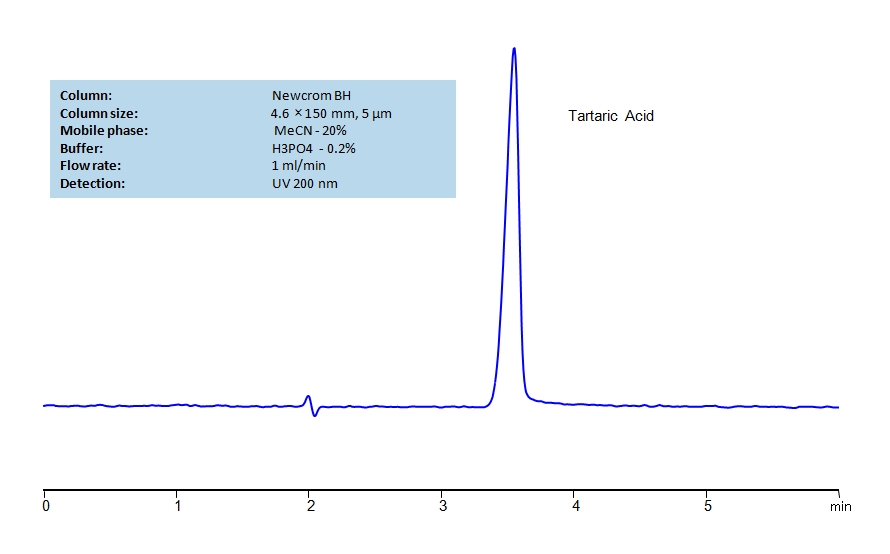
HPLC Method for Determination of Tartaric Acid on Newcrom BH Column
February 5, 2020
HPLC Method for Tartaric Acid on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Tartaric Acid.
Tartaric acid is a naturally occurring organic acid that is found in many plants, particularly in grapes and tamarinds. It’s known for its sour taste and antioxidant properties. Chemically, tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid. It has the chemical formula C4H6O6.
Tartaric acid has been used in winemaking for centuries because it plays a key role in the fermentation process. It’s also used in baking powder, where it serves as a leavening agent.
In addition to these culinary uses, tartaric acid is used in the manufacturing of effervescent salts, in combination with citric acid, to improve taste and make a fizz. It’s also found in some of the very effective rust removal and cleaning solutions.
Tartaric acid is used in cream of tartar (potassium bitartrate), which is used in cooking and baking. It can also be found in a variety of other foods, including soft drinks, fruit juices, candies, and ice cream.
Like other acids, tartaric acid can be hazardous in large quantities, and it should always be handled and stored appropriately. Always refer to the safety data sheet for this substance and follow the recommended safety guidelines.
Tartaric Acid can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom BH stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN) with a phosphoric acid buffer. Detection is performed using UV.
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 20/80% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 – 0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 200 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Hydrophilic |
| Analyzing Compounds | Tartaric Acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended

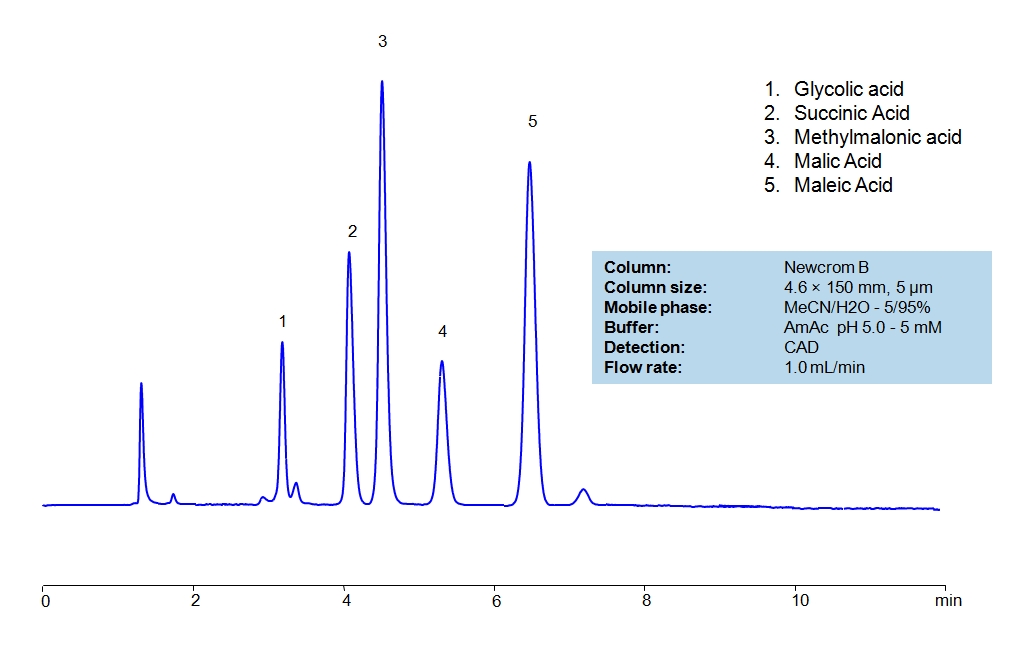
HPLC Separation of Small Organic Acids on Newcrom B Column
October 22, 2019
HPLC Method for Glycolic acid, Malic Acid, Maleic Acid, Methylmalonic Acid, Succinic Acid, Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid, Fumaric Acid, Citric Acid, Malonic Acid, Gluconic acid on Newcrom B by SIELC Technologies
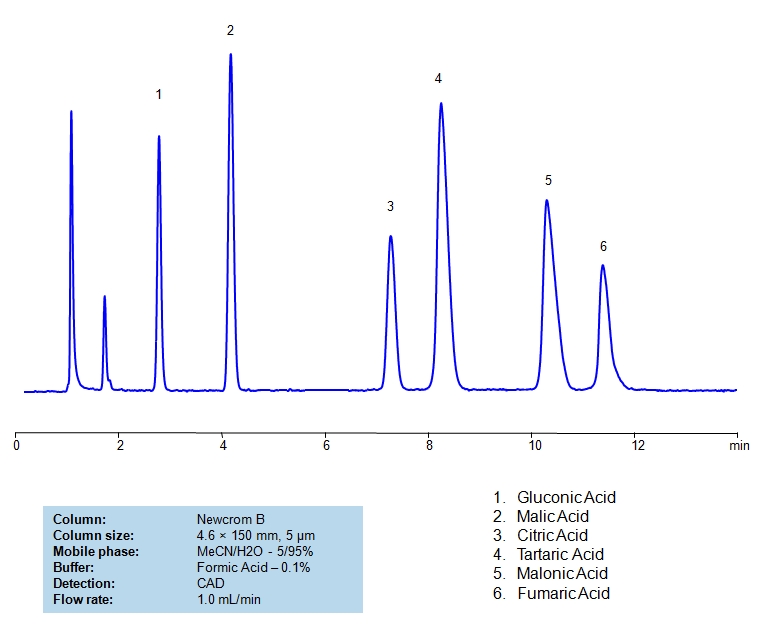
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Glycolic acid, Malic Acid, Maleic Acid, Methylmalonic Acid, Succinic Acid, Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid, Fumaric Acid, Citric Acid, Malonic Acid, Gluconic acid.
Gluconic Acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula C6H12O7. It is naturally found in fruits. Industrially, it is found in honey that is produced by fermenting starch. Typically, it is used in food, beverage, cosmetic, and skin care industries.
Malic Acid is an alpha hydroxy acid with the chemical formula C4H6O5. It is most commonly found in fruits and wines. It is sour, which is partially why it is often used as a food additive. Besides food, it is also used in skin-care as an exfoliant.
Citric Acid is a naturally occurring organic acid found in citrus fruits; it is also an intermediate in the citric acid cycle of aerobic organisms. It is used industrially as an acidity regulator, flavoring, detergent, and more than 2 million tons are produced annually. It’s chemical formula is C₆H₈O₇.
Tartaric Acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula C4H6O6. It is found in fruits like grapes and tamarinds and is a vital component of wine. It is also used in metal cleaning, as an antioxidant, and as an acidulant.
Malonic Acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C3H4O4. It is also known as cis-butenedioic acid. It is a trans counterpart of fumaric acid. It has a variety of uses from dyeing natural fibers to oil and fat preservative, to synthesis of hydrogels.
Fumaric Acid, also known as trans-butenedioic acid, is an organic compound with C4H4O4 chemical formula. It is used across Food, industrial, and medical industries. In food, is it often used as a preservative, pH regulator, and flavoring akin to citric acid. Industrially, it is used in making polyester resins, polyhydric alcohols, and more. Medically, it is used in denture cleaners and it’s derivatives are used in treating psoriasis.
Glycolic acid, Malic Acid, Maleic Acid, Methylmalonic Acid, Succinic Acid, Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid, Fumaric Acid, Citric Acid, Malonic Acid, Gluconic acid can be retained and analyzed using the Newcrom B stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water and acetonitrile (MeCN). Detection is performed using CAD.
| Column | Newcrom B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 5/95% |
| Buffer | AmAc pH 5.0, Formic Acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | CAD (Corona) MS- compatible mobile phase |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Glycolic acid, Malic Acid, Maleic Acid, Methylmalonic Acid, Succinic Acid, Tartaric Acid, dl-Tartaric acid, Fumaric Acid, Citric Acid, Malonic Acid, Gluconic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Fumaric Acid
Gluconic acid
Glycolic acid
Maleic Acid
Malic Acid
Malonic Acid
Methylmalonic Acid
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
dl-Tartaric acid

HPLC Analysis of Basic Drugs and Acidic Counter-Ions by Mixed-Mode Chromatography
July 16, 2009
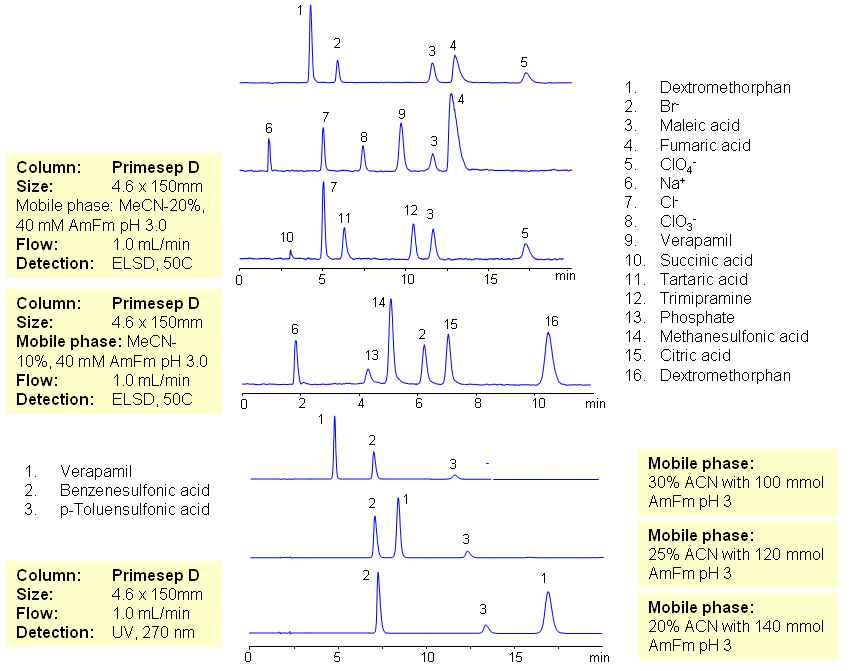
The majority of drugs in the pharmaceutical industry are administered in salt form. The presence of two counter-ions very often necessitates the use of two methods. The nature of these counterparts in drugs can be an inorganic cation and organic acid, inorganic anion and organic base, and organic cation and organic anion. Furthermore, the properties of the molecules will result in a differing stoichiometry. The task of simultaneous quantitation of counter-ions can be achieved by using mixed-mode columns. The general approach for analysis is based on properties of corresponding counter-ions. Hydrophobic basic drugs, like dextromethorphan, verapamil, trimipramine, and corresponding acidic counter-ions (chloride, chlorate, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, maleate, fumarate,tartrate, succinate, phosphate, citrate, benzosulfonate, toleuensulfonate) can be separated and quantitated in the same run on reversed-phase anion-exchange column. Basic hydrophobic drugs are retained by the reversed-phase mechanism, and counter-ions are retained by the reversed-phase and anion-exchange mechanism. Some polar counter-ions are retained only by the anion-exchange mechanism. Retention time and selectivity of HPLC separation of drugs and counter-ions can be achieved by changing the amount of acetonitrile and the amount of ions in the mobile phase. The detection technique depends on the properties of the counter-ions. In case of low or no UV activity, ELSD can be employed if the counter-ion forms a non-volatile salt with the mobile phase additive (ammonium formate). This HPLC method can be used for simultaneous quantitation of other basic drugs and counter-ions. The presence of two mechanisms of retention allows control over retention times of drug and counter-ion independently, and even allows a change of order of elution when necessary.
| Column | Primesep D , 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0 |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, UV 270 |
| Class of Compounds | Ions, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Base, Acids, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sodium Chloride, Sodium chloride, Sodium Chlorate, Sodium bromide, Sodium bromate, Perchloric Acid, Maleic Acid, Fumaric Acid, Tartaric Acid, Succinic Acid, Phosphoric Acid, Citric acid, Benzosulfonic acid, Dextromethorphan, Verapamil, Trimipramine |
Application Column
Primesep D
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsBromide
Chlorate
Chloride
Citric Acid
Dextromethorphan
Fumaric Acid
Maleic Acid
Organic Acids
Perchlorate
Phosphoric Acid
Pyrilamine
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid
Verapamil
p-Toluenesulfonic Acid (PTSA)
UV Detection

HILIC Separation of Carboxylic Acids
August 22, 2008
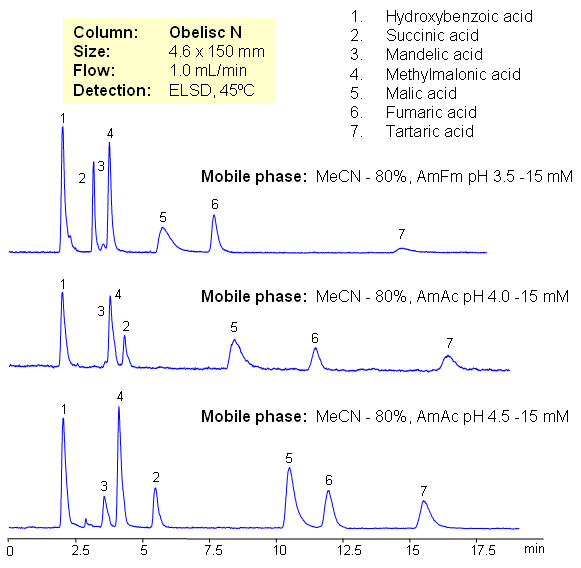
Hydrophilic acids are separated on Obelisc N mixed-mode HILIC column. Seven carboxylic acids are separated based on their polarity and pKa values. Changes in ionization states of acids and stationary phase can be used to control elution order of organic and inorganic acids.
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsHydroxybenzoic Acid
Malic Acid
Mandelic Acid
Methylmalonic Acid
Organic Acids
Succinic Acid
Tartaric Acid