| CAS Number | 474-25-9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 392.580 |
| InChI Key | RUDATBOHQWOJDD-BSWAIDMHSA-N |
| LogP | 3.00 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
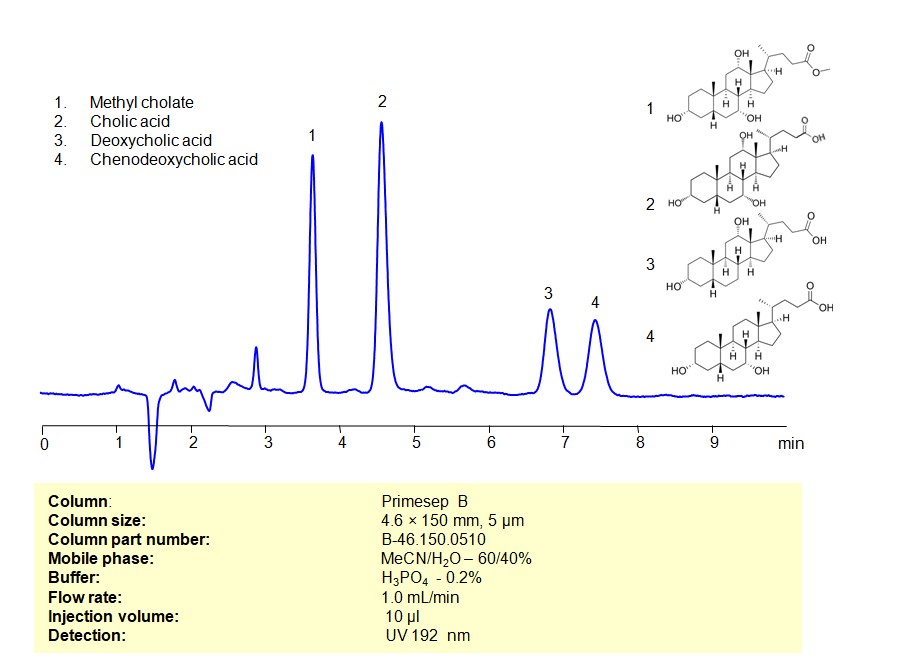
HPLC Method for Separation of Bile acids (Methyl cholate, Cholic acid, Deoxycholic acid, Chenodeoxycholic acid) on Primesep B Column
January 24, 2024
HPLC Method for Analysis of Methyl cholate, Cholic acid, Deoxycholic acid, Chenodeoxycholic acid on Primesep B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Methyl cholate, Cholic acid, Deoxycholic acid, Chenodeoxycholic acid
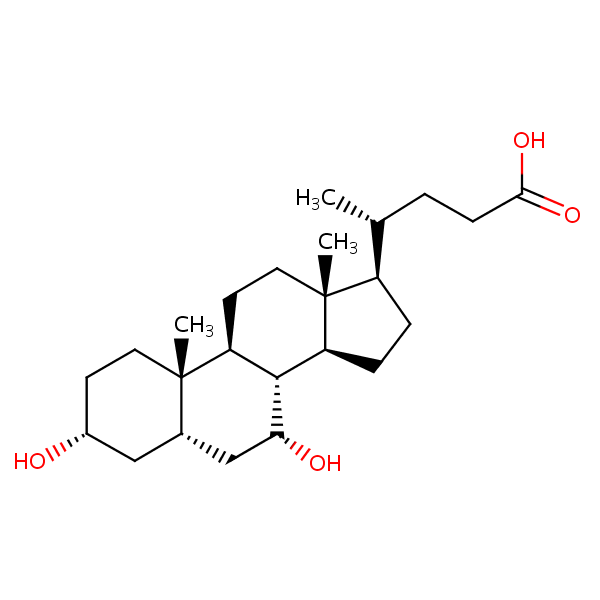
Bile acids are a class of amphipathic molecules derived from cholesterol that play a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. They are synthesized in the liver and released into the small intestine during digestion.
- Cholic Acid:
- Cholic acid is a primary bile acid.
- It is synthesized in the liver from cholesterol.
- Cholic acid contributes to the emulsification and digestion of fats in the small intestine.
- Deoxycholic Acid:
- Deoxycholic acid is a secondary bile acid.
- It is formed by bacterial action in the colon on cholic acid.
- Deoxycholic acid also aids in the digestion and absorption of fats.
- Chenodeoxycholic Acid:
- Chenodeoxycholic acid is another primary bile acid.
- It is synthesized in the liver.
- Like cholic acid, it participates in the emulsification of fats.
- Methyl Cholate:
- Methyl cholate is a derivative of cholic acid.
- It is formed by adding a methyl group to cholic acid.
- Bile acids, including methyl cholate, contribute to the solubilization of lipids.
These bile acids are part of the bile acid pool, which undergoes enterohepatic circulation—being released into the small intestine, reabsorbed in the terminal ileum, and returned to the liver. Bile acids also play a role in cholesterol metabolism and act as signaling molecules.
Their chemical structures, amphipathic nature, and interactions with lipids are essential for their physiological functions in the digestive process. The balance of bile acids in the body is crucial for proper digestion and absorption of dietary fats.
Bile acids can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a Primesep B mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. Detection is achieved using UV at 192 nm
| Column | Primesep B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 60/40% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 192 nm |
| Samples | 2 mg/mL in MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Injection volume | 10 µl |
| LOD* | 0.2 ppm |
| Class of Compounds | bile acids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Methyl cholate, Cholic acid, Deoxycholic acid, Chenodeoxycholic acid |
Application Column
Primesep B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Cholic acid
Deoxycholic acid
Methyl cholate

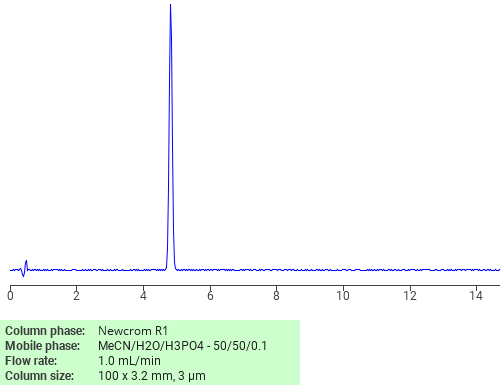
Separation of Chenodeoxycholic acid on Newcrom R1 HPLC column
February 16, 2018
Chenodeoxycholic acid can be analyzed by this reverse phase (RP) HPLC method with simple conditions. The mobile phase contains an acetonitrile (MeCN), water, and phosphoric acid. For Mass-Spec (MS) compatible applications the phosphoric acid needs to be replaced with formic acid. Smaller 3 µm particles columns available for fast UPLC applications. This liquid chromatography method is scalable and can be used for isolation impurities in preparative separation. It also suitable for pharmacokinetics.
Application Column
Newcrom R1
The Newcrom columns are a family of reverse-phase-based columns. Newcrom A, AH, B, and BH are all mixed-mode columns with either positive or negative ion-pairing groups attached to either short (25 Å) or long (100 Å) ligand chains. Newcrom R1 is a special reverse-phase column with low silanol activity.
Select options