| Synonyms |
|---|
Applications:
HPLC ELSD Method for Analysis of Arachidonoyl ethanolamideand Arachidonic acid on Lipak Column
December 18, 2024
HPLC Method for Arachidonic acid (AA), Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) on Lipak by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Arachidonic acid (AA), Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA)
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) and arachidonic acid (AA) are closely related bioactive lipids that play significant roles in various physiological and biochemical processes.
Arachidonic acid, a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid, is a critical precursor for the biosynthesis of prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. In cells, nearly all arachidonic acid is stored as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids, with its levels tightly regulated through interconnected metabolic pathways. Upon stimulation, free arachidonic acid is transiently released, serving as a vital substrate for the production of eicosanoid signaling molecules. Processes such as receptor-mediated release, metabolic transformation, and reuptake of free arachidonate are essential for cell signaling and inflammatory responses.
Precursor Relationship: AEA is synthesized from arachidonic acid via enzymatic pathways. AA is first converted to N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE), then cleaved to form AEA.Biological Cross-Talk:
- Both AEA and AA influence inflammatory and pain pathways.
- AEA’s degradation contributes to free arachidonic acid pools, linking endocannabinoid signaling with eicosanoid production.
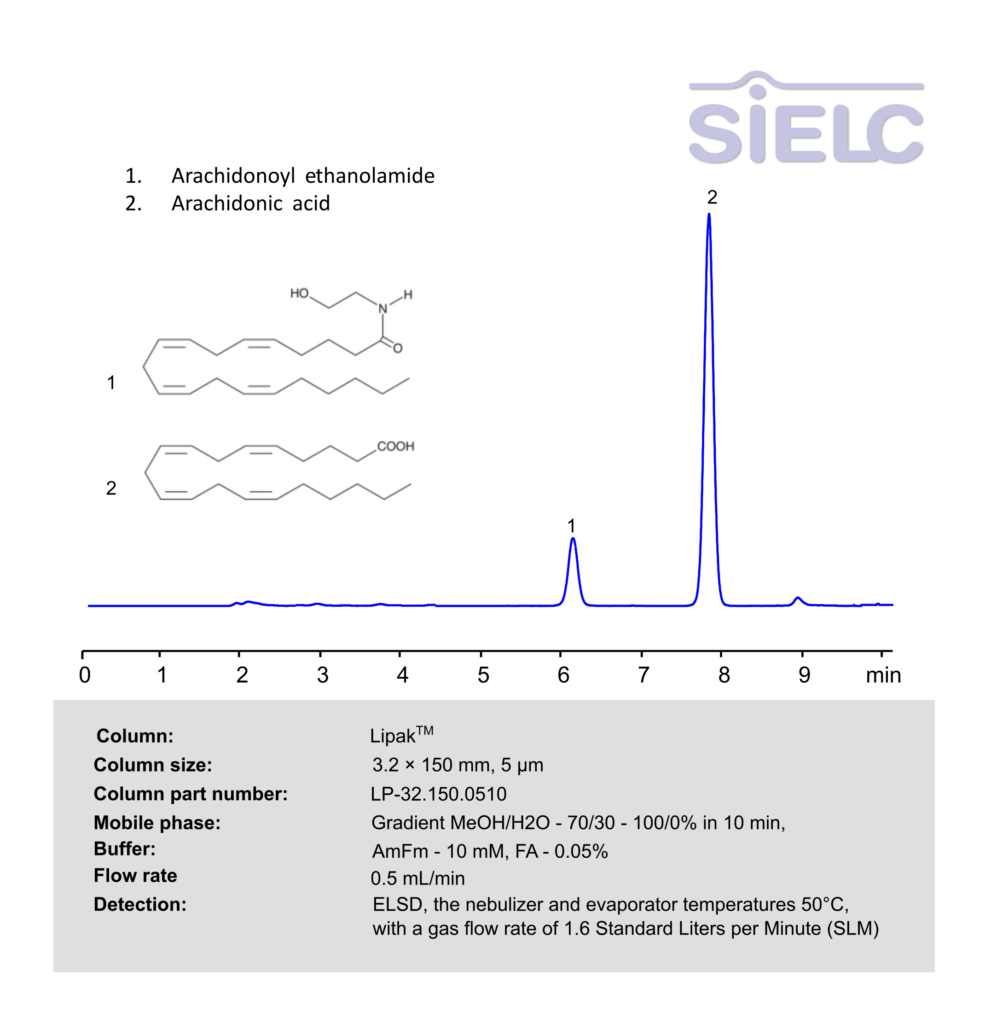
Arachidonic acid (AA), Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) can be retained, and analyzed using a Lipak mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an gradient method with a mobile phase consisting of water, methanol (MeOH), ammonium formate and formic acid as a buffer. Detection is achieved using ELSD
| Column | Lipak, 3.2 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeOH/H2O – 70/30 – 100/0% in 10 min |
| Buffer | AmFm– 10 mM, FA – 0.05% |
| Flow Rate | 0.5 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 50°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM) |
| Class of Compounds | Endocannabinoids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Arachidonic acid (AA), Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) |
Application Column
Lipak
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA)


