Alltesta HPLC Method for Tyramine on Primesep 100 by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Tyramine
Tyramine is a naturally occurring compound derived from the amino acid tyrosine. It is found in various foods and beverages, especially aged or fermented products such as aged cheeses, cured meats, certain wines, and soy products. Tyramine can affect the release of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter, and can influence blood pressure.
For people taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), consuming foods high in tyramine can cause a dangerous spike in blood pressure, known as a hypertensive crisis. This is why individuals on such medications are often advised to follow a low-tyramine diet.
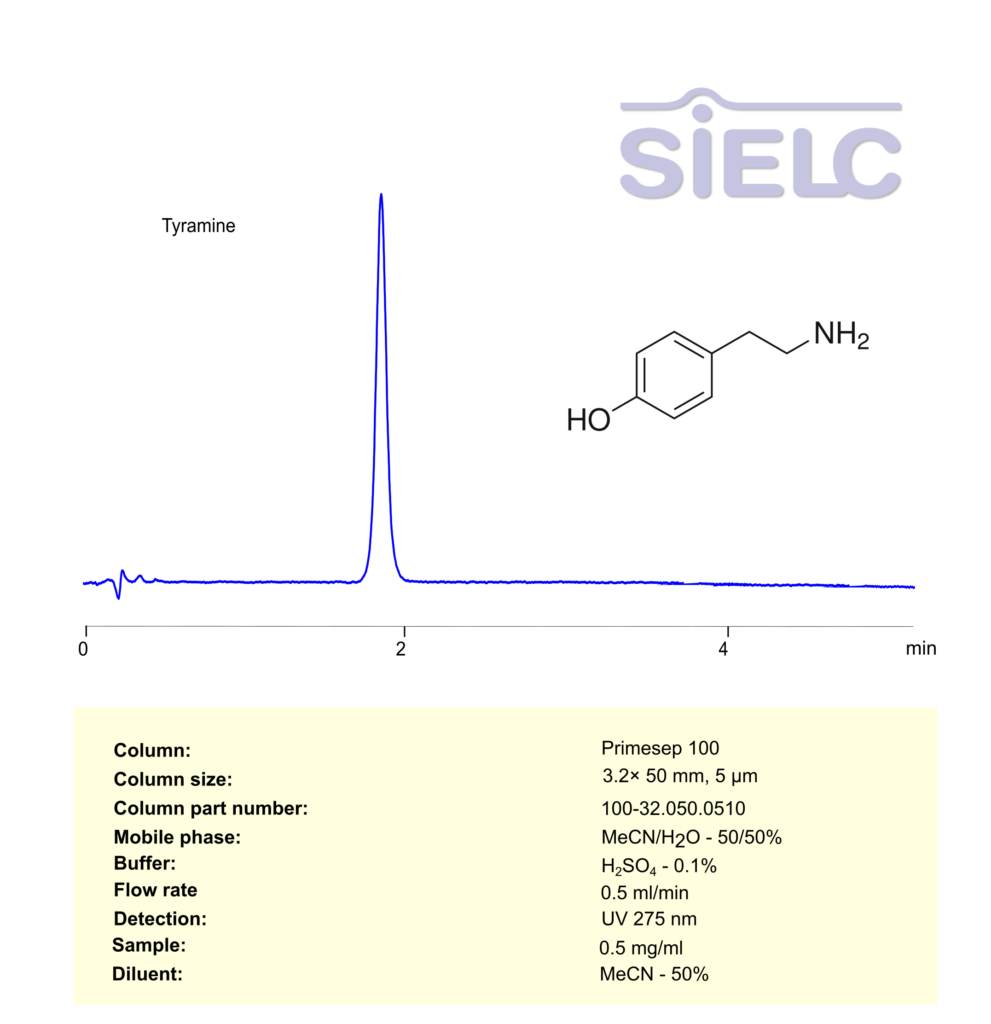
Tyramine can be retained, and analyzed using a Primesep 100 mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. Detection is achieved using UV at 275 nm
| Column | Primesep 100, 3.2 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 -0.1% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 275 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Amine |
| Analyzing Compounds | Tyramine |
You can view examples of chromatograms obtained using the Allesta instrument and Sielc columns by clicking here.
Application Column
Primesep 100
Column Diameter: 3.2 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





