 |
Solid-Core Mixed-Mode Stationary Phases |
SIELC Technologies has developed mixed-mode Columns based on solid-core-porous-shell particles. This separation media combines the efficiency of solid-core technology with the unique selectivity of Ion-Exchange (IE), reverse phase (RP), surface chemistry and ion-exchange HILIC surface.
Combination of solid core particles and IE with RP or HILIC chemistry offers:
- Fast separation
- Working pressure within limits of conventional HPLC
- Unique selectivity profile
- Retention of compounds difficult to retain by RP chromatography
- Increase column loading capacity
- Adjustment of selectivity by mobile phase pH, ion strength, and organic concentration and composition
Columns available in Solid-Core format with 2.7 µm particles:
| Column | Ion-exchange | Separation mode |
| Primesep 100 | Cation exchange | RP |
| Primesep SB | Anion exchange | RP |
| Primesep S | Cation exchange | HILIC |
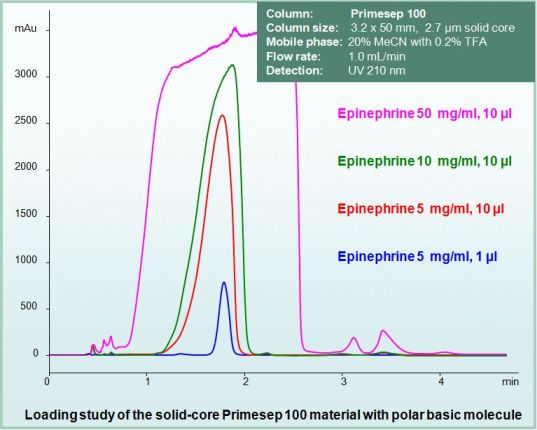
One disadvantage of the solid core support in HPLC is lower capacity when you compare it to regular through porous material. However, the mixed-mode materials demonstrated much higher loading capacity compared to regular RP phases (Nicola H. Davies, Melvin R. Euerby and David V. McCalley, Journal of Chromatography A, Volume 1138, Issues 1-2, 5 January 2007, 65-72). Thus, the mixed-mode surface chemistry compensates for loss of loading capacity of partially non-porous particles.
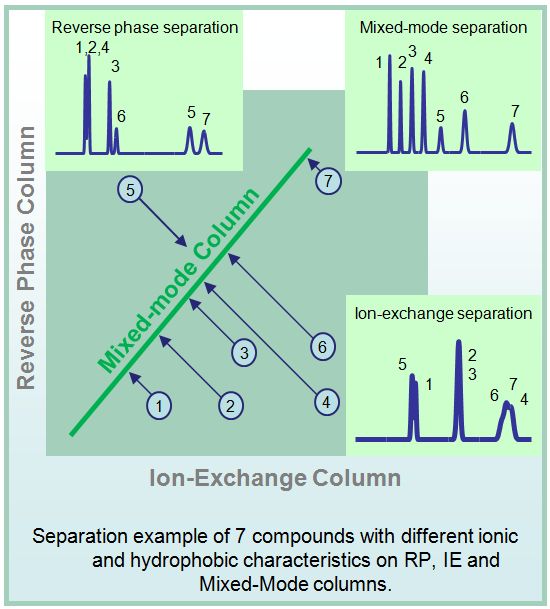
Mixed mode columns demonstrate 2D characteristics with independent adjustment of degree of retention based on ionic and hydrophobic mechanism
Reverse phase mechanism controls by amount of organic modifier in the mobile phase
Ion-exchange mechanism controls by ion strength and pH of the mobile phase
This property allows to resolve complex mixtures with polar, hydrophobic, ionic, and neutral compounds
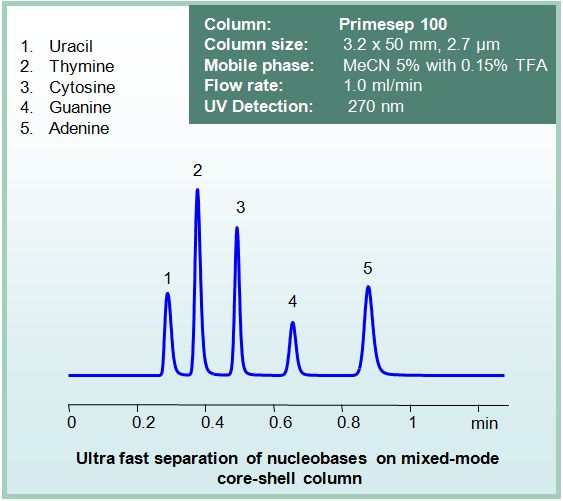
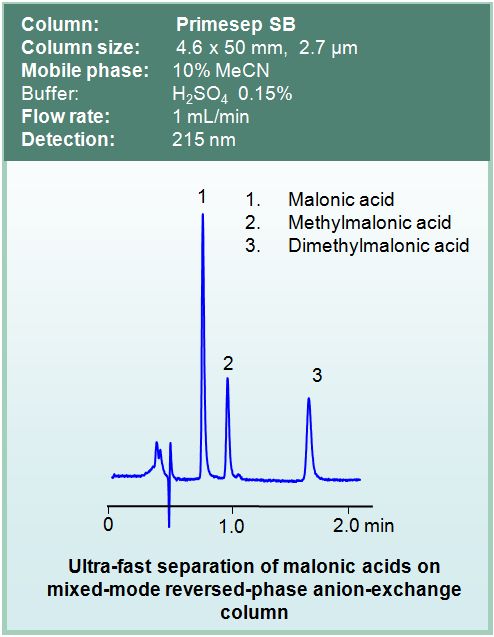
Some separation examples: