HPLC Method for Analysis of Trichloroacetic acid on BIST A+ Column by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Reversed-phase
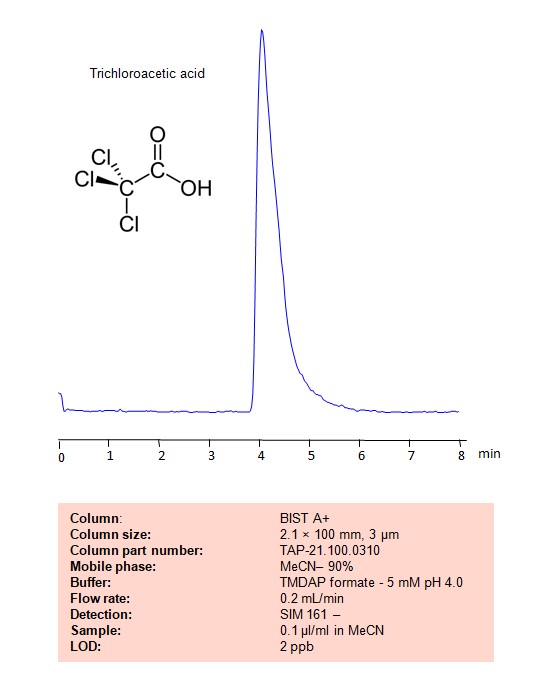
Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) is a chemical compound with the formula CCl3COOH. It is a strong organic acid and a derivative of acetic acid, where three of the four hydrogen atoms in the methyl group of acetic acid are replaced by chlorine atoms.
Trichloroacetic acid is commonly used in various applications, including:
Chemical Synthesis: TCA serves as a reagent in various chemical reactions, such as the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides.
Protein Precipitation: In biochemistry and molecular biology, TCA is often used for the precipitation of proteins from solution. It is particularly useful for removing proteins from samples for further analysis.
Skin Care: TCA is also used in dermatology as a peeling agent to treat various skin conditions, including acne scars, sun damage, and wrinkles. It promotes exfoliation and the regeneration of skin cells.
DNA and RNA Precipitation: TCA is employed to precipitate nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) from solution, facilitating their isolation and purification in molecular biology experiments.
Trichloroacetic acid is corrosive and should be handled with care.
Trichloroacetic acid can be retained and analyzed on a BIST A+ column using an analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN) , and a TMDAP formate as a buffer. This analysis method can be detected using LC MS.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analyses of Trichloroacetic acid on BIST A+ Column by SIELC Technologies
Condition
| Column | BIST A+, 2.1 x 100 mm, 3 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 90/10% |
| Buffer | TMDAP formate – 5 mM pH 4.0 |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | SIM 161- |
| Sample | 0.1µl/ml |
| LOD* | 2 ppb |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Bis-biguanide |
| Analyzing Compounds | Trichloroacetic acid |
Application Column
BIST A+
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 3 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





