Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sucrose octasulfate on BIST A+ Column by SIELC Technologies
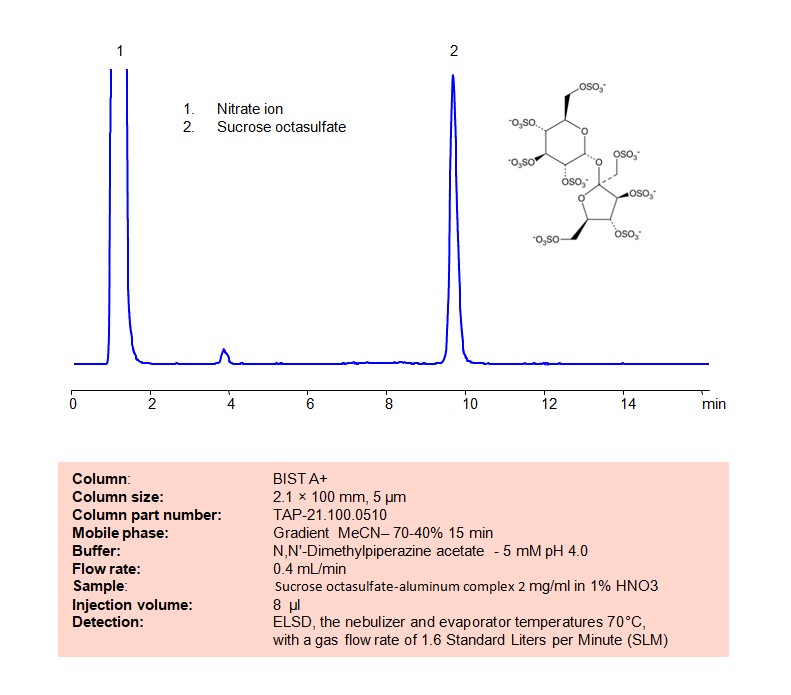
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sucrose octasulfate
he Sucrose octasulfate-aluminum complex is a chemical compound where sucrose octasulfate, a derivative of sucrose with eight sulfate groups, forms a complex with aluminum ions. This complex exhibits unique properties due to the interaction between the sulfated sugar and aluminum.
Structure and Composition: In this complex, aluminum ions interact with the sulfate groups of sucrose octasulfate. The exact structure depends on the ratio of sucrose octasulfate to aluminum and the conditions under which the complex is formed.
Properties: The combination of a large, organic, sulfated molecule with a metal ion like aluminum can result in changes in solubility, stability, and reactivity compared to the individual components. The properties of such complexes can be quite different from those of either sucrose octasulfate or aluminum alone.
Applications: Such complexes can have various applications depending on their specific properties. They might be used in medicinal or pharmaceutical formulations, particularly where the interaction between a metal ion and an organic compound is beneficial. For instance, they could have applications in drug delivery, wound healing, or as components in medical devices.
Biological Interactions: The presence of both organic (sucrose octasulfate) and inorganic (aluminum) components can influence how this compound interacts with biological systems. For example, it might have specific binding properties or biological activity that are leveraged in therapeutic contexts.
Environmental and Health Considerations: As with any compound containing metal ions, there are considerations regarding environmental impact and human health, especially regarding the bioavailability and toxicity of aluminum.
Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, sucrose octasulfate can be retained on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A column. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as Dimethyl piperazine acetate, which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively charged dye to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Using this new and unique analysis method, oligonucleotide can be separated, retained, and detected at ELSD
Please read more on oligonucleotides analysis by HPLC in our April’s 2023 newsletter.
Condition
| Column | BIST A+, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | Gradienr MeCN – 70-40%, 15 min |
| Buffer | DMP acetate pH 4.0 – 5 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, the nebulizer and evaporator temperatures 70°C, with a gas flow rate of 1.6 Standard Liters per Minute (SLM |
| Sample | 2 mg/ml in 1% HNO3 |
| Injection volume | 8 µl |
| LOD* |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Sulfated polysaccharides |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sucrose octasulfate |
Application Column
BIST A+
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





