HPLC Method for Analysis of Methyl cholate on Primesep B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Methyl cholate
Methyl cholate is a compound that belongs to the class of bile acids. Bile acids are substances that are produced by the liver and play a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Cholate is a primary bile acid, and when methylated, it forms methyl cholate.
- Methyl cholate is derived from cholic acid, one of the primary bile acids. The addition of a methyl group to cholic acid results in the formation of methyl cholate.
- Bile acids, including cholic acid and its derivatives like methyl cholate, aid in the emulsification and digestion of fats in the small intestine. They also play a role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
- Bile acids, including methyl cholate, undergo complex metabolic pathways in the liver and are released into the small intestine during digestion to aid in the breakdown of fats.
It’s important to note that bile acids have physiological roles beyond digestion, including the regulation of cholesterol metabolism and acting as signaling molecules.
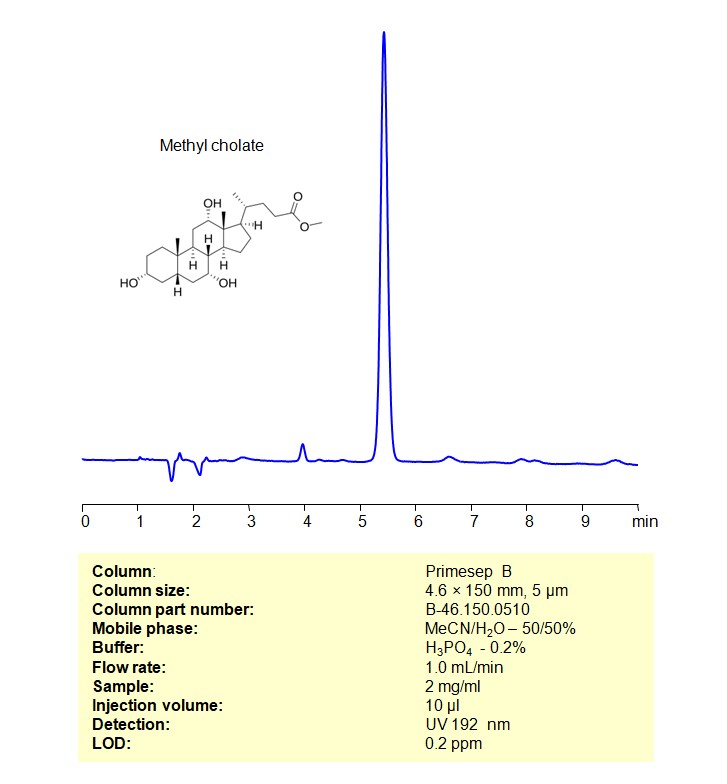
Methyl cholate can be retained and analyzed using a Primesep B mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis employs an isocratic method with a simple mobile phase comprising water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. This method allows for detection using UV at 192 nm
| Column | Primesep B, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Buffer | H3PO4 -0.2% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | UV 192 nm |
| Samples | 2 mg/mL in MeCN/H2O – 50/50% |
| Injection volume | 10 µl |
| LOD* | 0.2 ppm |
| Class of Compounds | bile acids |
| Analyzing Compounds | Methyl cholate |
Application Column
Primesep B
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended





