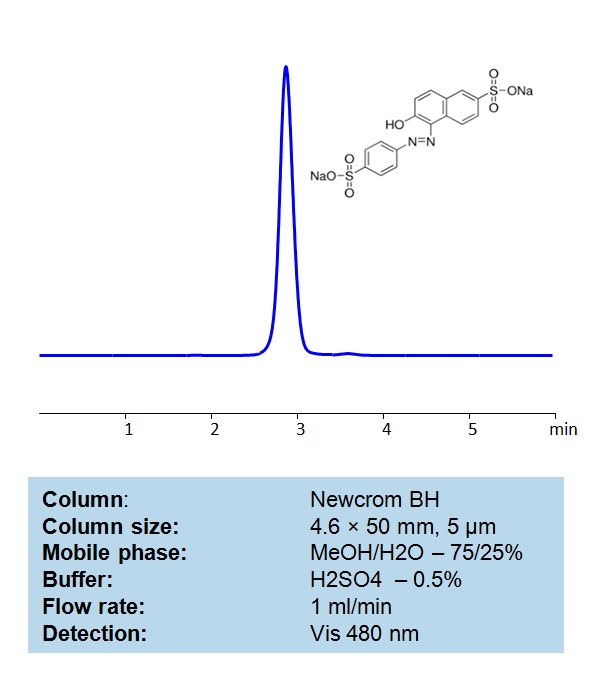
HPLC Method for Sunset Yellow (Yellow 6) on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sunset Yellow (Yellow 6).
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 50 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeOH/H2O – 75/25% |
| Buffer | H2SO4 – 0.5% |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | Vis 480 nm |
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Dyes |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sunset Yellow (Yellow 6) |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 50 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Application Analytes:
Sunset Yellow (Yellow 6)Application Detection:
Vis Detection
SIELC Technologies usually develops more than one method for each compound. Therefore, this particular method may not be the best available method from our portfolio for your specific application. Before you decide to implement this method in your research, please send us an email to research@sielc.com so we can ensure you get optimal results for your compound/s of interest.