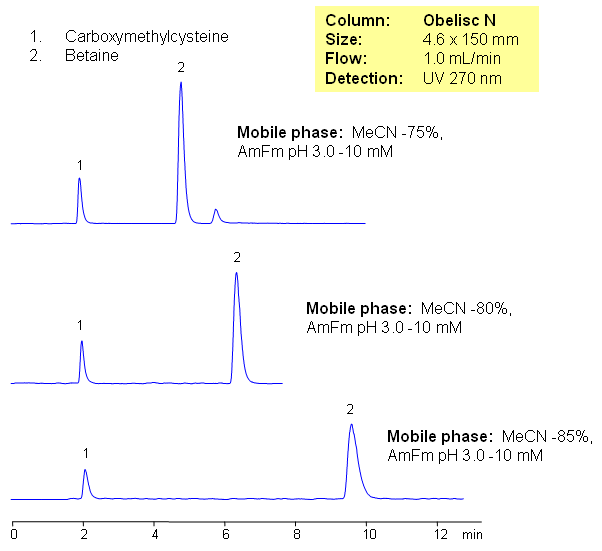
In this HPLC method, betaine and carboxymethylcysteine are separated by HILIC mixed-mode mechanism. Betaine and carboxymethylcysteine are very hydrophilic compounds which are not retained on reverse phase columns. Compounds are separated by combination of HILIC and ion-exchange mechanisms. In HIILIC mode, Obelisc N columns allow operating at lower organic concentration for improved solubility of analytes. Method can be used for quantitative or qualitative analysis of betaine and carboxymethylcysteine using ESLD or LC/MS detection. Betaine in chemistry is any neutral chemical compound with a positively charged cationic functional group such as ammonium ion or phosphonium ion (generally: onium ions) which bears no hydrogen atom and with a negatively charged functional group such as a carboxylate group which may not be adjacent to the cationic site. Historically the term was reserved for tetramethylglycine only.
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsCarboxymethylcysteine
UV Detection





