| CAS Number | 512-69-6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H32O16 |
| Molecular Weight | 504.438 |
| InChI Key | MUPFEKGTMRGPLJ-ZQSKZDJDSA-N |
| LogP | -3.34 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
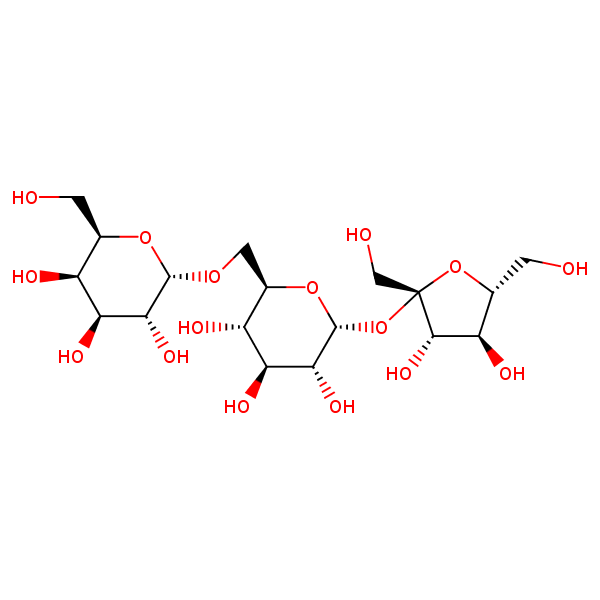
Separation of Trisaccharides on Obelisc N Column
July 6, 2015
Trisaccharides can be difficult to separate using conventional HPLC columns. The four trisaccharides panose, raffinose, isomaltotriose, and kestose have the same chemical formula, and the all have two glycosidic bonds connecting the three monosaccharides. Obelisc N was used as a stationary phase to separate trisaccharides because it is capable of multiple modes of separation. Obelisc N is a highly polar column that retains polar and charged analytes. Even though the trisaccharides differ only in regio- and stereochemistry they are resolved.
| Column | Obelisc R, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 75% |
| Buffer | AmFm pH 3.0- 10 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Trisaccharides, Hydrophilic, Ionizable |
| Analyzing Compounds | Raffinose, Kestose, Panose, Isomaltose |
Application Column
Obelisc N
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Kestose
Panose
Raffinose

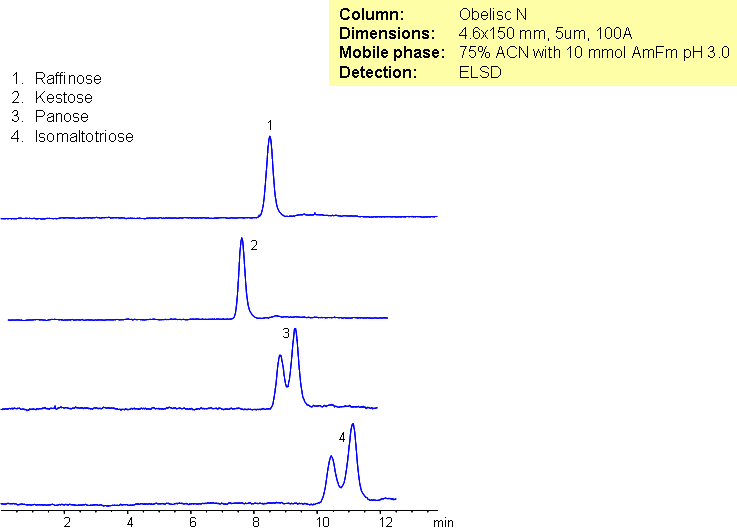
HPLC Separation of Sugars on Primesep S2 Column
July 14, 2011
Five sugars were separated on a Primesep S2 HILIC column with LC/MS compatible conditions. Various mobile phase produce different selectivity and separation. Method can be used as alternative to aminopropyl column. Primesep S2 column is stable and does not undergo rapid hydrolysis like aminopropyl columns.
| Column | Primesep S2, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmAc pH 5.0, Formic Acid |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD 50C |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Monocarboxylic acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Hormone |
| Analyzing Compounds | Fructose, Glucose, Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose, Sorbitol, Sucrose, Alfa D-Lactose, Beta D–Lactose, Raffinose |
Application Column
Primesep S2
The Primesep family of mixed-mode columns offers a wide variety of stationary phases, boasting unprecedented selectivity in the separation of a broad array of chemical compounds across multiple applications. Corresponding Primesep guard columns, available with all stationary phases, do not require holders. SIELC provides a method development service available to all customers. Inquire about our specially-tailored custom LC-phases for specific separations.
Select optionsGlucose
Lactose
Maltose
Raffinose
Sorbitol
Sucrose
alpha-D-Lactose
beta-D-Lactose

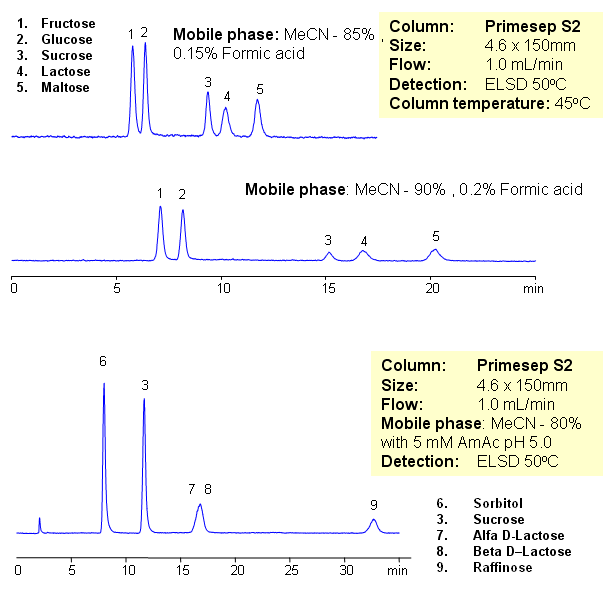
HILIC Separation of Sugars on Obelisc N
March 3, 2010
Common sugars can be separated on an Obelisc N HILIC/cation-exchange column with LC/MS compatible mobile phase. Highly polar surface of Obelisc N column provides good retention for sorbitol, sucrose, lactose and raffinose. Other sugars can be separated using this column.
| Column | Obelisc N, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmFm |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Sugars |
| Analyzing Compounds | Sorbitol, Sucrose, Lactose, Raffinose |
Application Column
Obelisc N
SIELC has developed the Obelisc™ columns, which are mixed-mode and utilize Liquid Separation Cell technology (LiSC™). These cost-effective columns are the first of their kind to be commercially available and can replace multiple HPLC columns, including reversed-phase (RP), AQ-type reversed-phase, polar-embedded group RP columns, normal-phase, cation-exchange, anion-exchange, ion-exclusion, and HILIC (Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography) columns. By controlling just three orthogonal method parameters - buffer concentration, buffer pH, and organic modifier concentration - users can adjust the column properties with pinpoint precision to separate complex mixtures.
Select optionsSorbitol
Sucrose
alpha-D-Lactose
beta-D-Lactose

Effect of Both pH and Organic Content on a Separation of Sugars, Amino Acids, and Carboxylic Acids
March 3, 2010
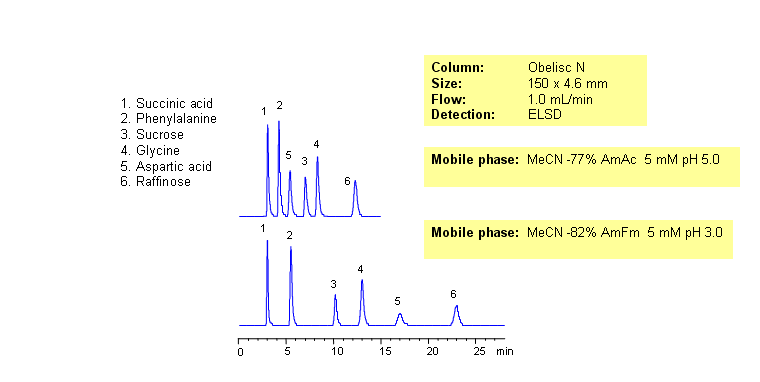
In mixed-mode HILIC chromatography, selectivity of separation can be adjusted by amount of acetonitrile, amount of buffer and buffer pH. Buffer concentration and pH will affect retention of ionizable compounds to a different degree. Retention of neutral compounds can be adjusted by the amount of acetonitrile. Carboxylic acid, three amino acids and two sugars are separated by combination of HILIC and ion-exchange mechanisms. Compounds can be monitored by ELSD, Corona (CAD), LC/MS or low UV. UV-transparent mobile phase /buffer is required for UV monitoring of this mixed-mode separation. This HPLC method can be adopted as general approach for analysis of sugars, amino acids and carboxylic acids.
| Column | Obelisc N, 4.6×150 mm, 5 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O |
| Buffer | AmAc |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD |
| Class of Compounds |
Drug, Acid, Hydrophilic, Ionizable, Vitamin, Supplements, Amino acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Succinic Acid, Phenylalanine, Sucrose, Glycine, Aspartic Acid, Raffinose |
Application Column
Obelisc N
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 150 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Phenylalanine
Raffinose
Succinic Acid
Sucrose