HPLC Method for Analysis of Fluconazole on Primesep B by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used to treat and prevent various fungal infections. Here are some key points about fluconazole:
1. Mechanism of Action:
- Fluconazole belongs to a class of drugs known as triazole antifungals. It works by inhibiting a fungal enzyme crucial for producing ergosterol, a key component of the fungal cell membrane. Without ergosterol, the fungal cell membrane becomes leaky and the fungal cells die, leading to the clearance of the infection.
2. Indications (Uses):
- Candidiasis: Fluconazole is often prescribed for vaginal yeast infections, which are caused by the fungus Candida. It’s also used for oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush), systemic candidiasis, and other Candida infections.
- Cryptococcal Meningitis: This is a serious fungal infection of the brain and spinal column, commonly seen in individuals with HIV/AIDS. Fluconazole can be used for treatment and to prevent a recurrence.
- Prophylaxis: In certain at-risk populations, like those with weakened immune systems or patients undergoing bone marrow transplants, fluconazole can be given to prevent fungal infections.
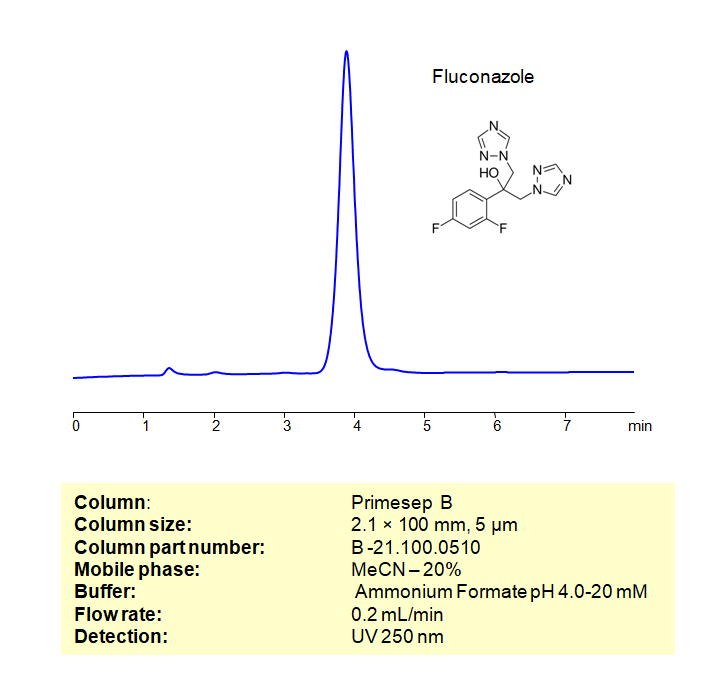
Fluconazole can be retained, and analyzed on a Primesep B mixed-mode stationary phase column using an isocratic analytical method with a simple mobile phase of water, Acetonitrile (MeCN), and a ammonium format a buffer. This analysis method can be detected in the UV 270 nm.
| Column | Primesep B, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 20% |
| Buffer | Ammonium Formate pH 4.0-20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | UV, 250 nm |
| Peak Retention Time | 3.97 min |
| Class of Compounds | Allylamines |
| Analyzing Compounds | Fluconazole |
Application Column
Primesep B
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A