HPLC Method for Analysis of Metamizole, Methylaminoantipyrine on Primesep SB by SIELC Technologies
Metamizole, also known as Analgin or dipyrone, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic widely used for the treatment of pain, fever, and spasms. It belongs to the pyrazolone class of drugs and is valued for its strong analgesic and spasmolytic properties. Unlike NSAIDs, Metamizole has minimal anti-inflammatory effects, making it distinct in its mechanism of action. However, its use is restricted or banned in some countries due to the risk of agranulocytosis, a rare but serious blood disorder.
After administration, Metamizole undergoes rapid hydrolysis in the body, forming its active metabolite 4-Methylaminoantipyrine (4-MAA). This metabolite is primarily responsible for the drug’s analgesic and antipyretic effects. 4-MAA is further metabolized into other derivatives, such as 4-Formylaminoantipyrine (4-FAA) and 4-Acetylaminoantipyrine (4-AAA), which contribute to the overall pharmacological activity of Metamizole.
Despite safety concerns, Metamizole (Analgin) remains widely used in several countries, particularly in Europe, Latin America, and parts of Asia, due to its effectiveness in managing moderate to severe pain. Ongoing research continues to evaluate its safety profile, mechanisms of action, and potential therapeutic applications.
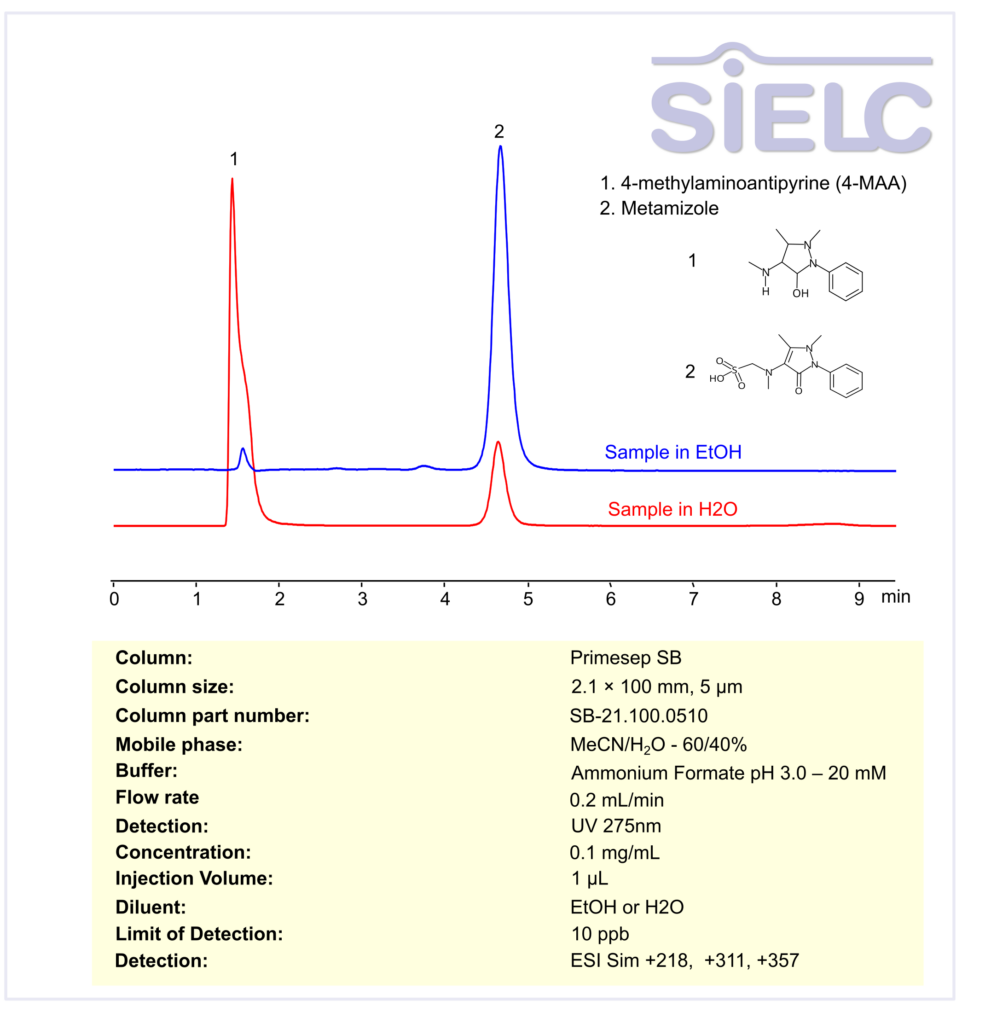
Metamizole, Methylaminoantipyrine can be retained, and analyzed using a Primesep B mix mode stationary phase column. The analysis utilizes a isocratic method with a simple mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium formate as a buffer. Detection is carried out using UV.
| Column | Primesep SB, 2.1 x 100 mm, 5 µm, 100 A, dual ended |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN/H2O – 60/40% |
| Buffer | Ammonium Formate pH 3.0 – 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.2 ml/min |
| Detection | UV at 275 nm; ESI-SIM: [M+H]⁺ 218, 311, 357 |
| Class of Compounds | Drug |
| Analyzing Compounds | Metamizole, Methylaminoantipyrine |
Application Column
Primesep SB
Column Diameter: 2.1 mm
Column Length: 100 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
Column options: dual ended
Methylaminoantipyrine





