| Column inner diameter, mm | Column length, mm | Amount of silica, g | Column ion-exchange capacity, mMol | Amount of buffer in mL with concentration mMol requires to replace column contra Ions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mMol | 20 mMol | 50 mMol | ||||
| 4.6 | 250 | 3.7 | 1.9 | 225 | 115 | 45 |
| 4.6 | 150 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 135 | 70 | 30 |
| 4.6 | 50 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 45 | 25 | 10 |
| 3 | 250 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 100 | 50 | 20 |
| 3 | 150 | 1 | 0.5 | 60 | 30 | 15 |
| 3 | 50 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 20 | 10 | 5 |
| 2 | 250 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 45 | 25 | 10 |
| 2 | 150 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 30 | 15 | 10 |
| 2 | 50 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
Changing the Ionic Mobile Phase Modifier
|
Changing the ionic modifier requires replacement of all the ions in the mobile phase. In some cases it requires the replacement of all of the ions in mobile phase and all of the ions adsorbed in the column stationary phase. In the second case, a significantly higher amount of buffer is required to equilibrate the column.
|
|
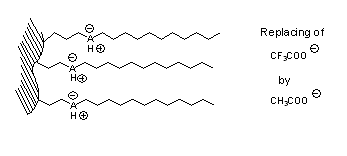 |
Buffers contain both anions and cations. If a cation exchange column is equilibrated with a new buffer that contains all of the same components other than the anion component, then it takes a small amount of buffer to complete the equilibration process (i.e. TFA replaced by AcOH).
|
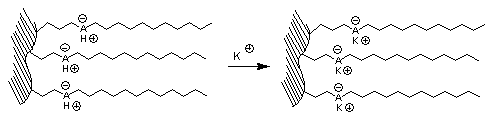 |
If a cation exchange column is equilibrated with a new buffer that contains a new cation component, then it takes a significantly larger amount of buffer to complete the equilibration process (i.e. NH replaced by NaAc).
|
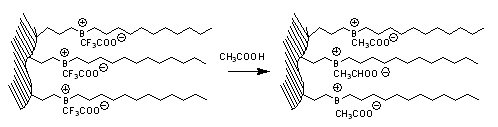 |
If an anion exchange column is equilibrated with a new buffer that contains a new anion component, then it also takes a large amount of buffer to complete the equilibration process (i.e. TFA replaced by AcOH). |
