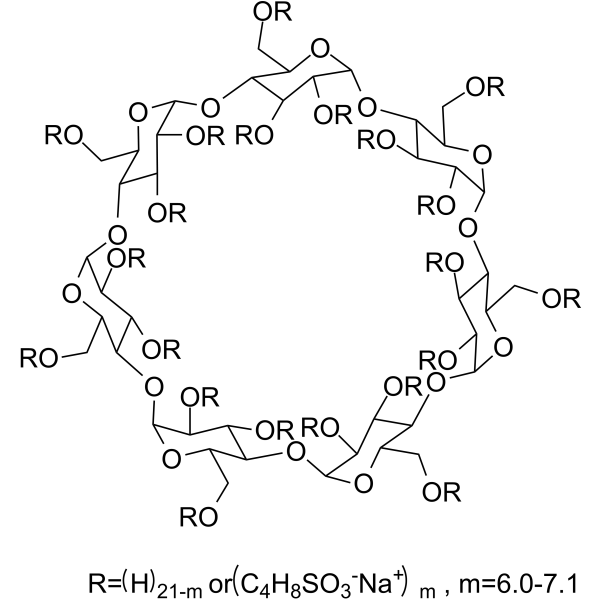
| Molecular Formula | C50H84Na2O41S2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1451.3 |
| InChI Key | RGQYVQYXCZODQW-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
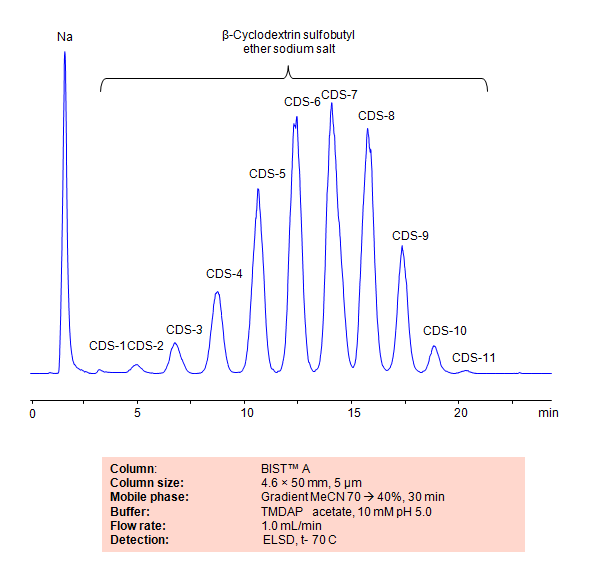
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sulfobutyl ether Beta Cyclodextrin Sodium (SBECD) on BIST™A Column
July 8, 2022
| Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ | ||||||||||||||
| HPLC Method for Analysis of B-Cyclodextrins sulfobutyl ether on a BIST™A Column.
|
||||||||||||||
|
Application Column
BIST A
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select options