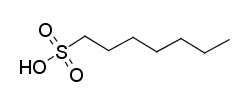
| CAS Number | 60586-80-3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H16O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 180.27 |
| InChI Key | AKRQHOWXVSDJEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2 |
| Synonyms |
|
Applications:
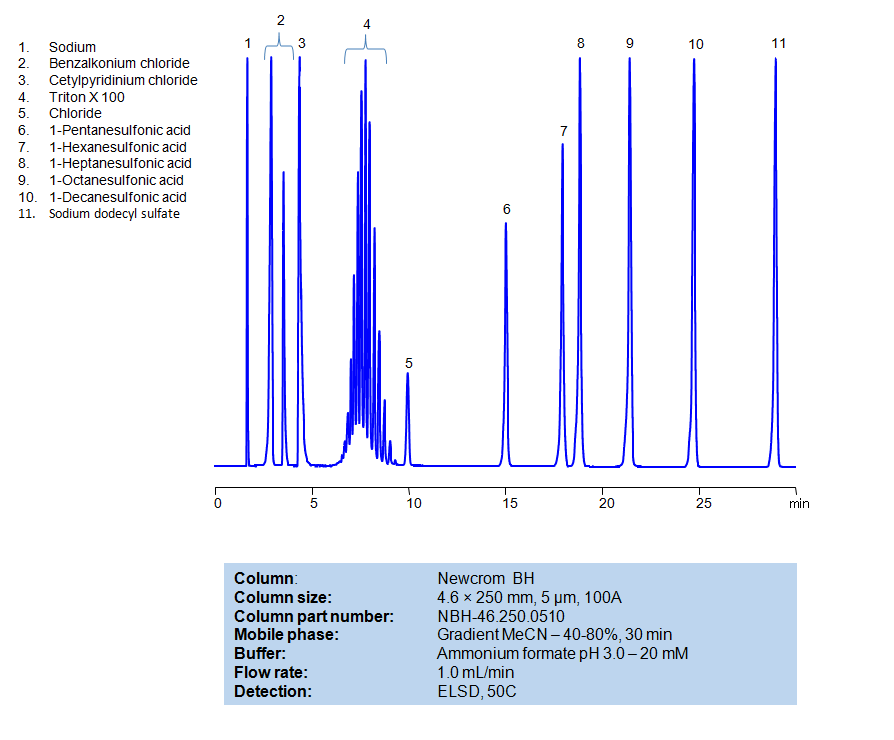
HPLC Method for Separation of Hydrotopic, Cationic, Nonionic and Anion Surfactants on Newcrom BH Column
July 10, 2023
HPLC Method for Analysis of Hydrotopic, Cationic, Nonionic and Anion Surfactants on Newcrom BH by SIELC Technologies
Separation type: Liquid Chromatography Mixed-mode
Surfactants, also known as surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension (or interfacial tension) between two liquids or between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants.
They are often classified according to the charge of the polar head group:
Anionic Surfactants: These surfactants have a negative charge on their polar head group. Common examples include soap, sodium laureth sulfate, and sodium lauryl sulfate. They are commonly used in detergents and shampoos due to their ability to emulsify oils and hold dirt in suspension, so it can be rinsed away.
Cationic Surfactants: These surfactants have a positive charge on their polar head group. Examples include cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and benzalkonium chloride. These are often used as antiseptics and can also be found in hair conditioners because they reduce static cling.
Nonionic Surfactants: These surfactants have no charge on their polar head group. Examples include alcohol ethoxylates, nonylphenol ethoxylates, and polysorbates. Nonionic surfactants are often used in laundry and dishwasher detergents.
Hydrotropic Surfactants: While not a category of charge like the others, hydrotropic surfactants are a distinct class that promote the solubility of other solutes in water. Sodium xylene sulfonate and sodium cumene sulfonate are examples of hydrotropes.
The selection of a specific type of surfactant depends on the specific application and the properties of the surfactant. Some surfactants can be aggressive and irritating to skin or eyes (like certain anionic surfactants), while others are milder. Similarly, some are better at emulsifying oil or suspending dirt, while others might provide good foaming action or work better in hard water.
All compounds can be retained, separated, and analyzed using a reverse-phase Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A column. The mobile phase for this method consists of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and Ammonium formate, which serves as a buffer. This analytical method can be detected with an Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (ELSD) or any other evaporative detection method (CAD, ESI-MS).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, Triton X100, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, 1-Hexanesulfonic acid, sodium salt, 1-Heptanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Octanesulfonic acid
Condition
| Column | Newcrom BH, 4.6 x 250 mm, 5 µm, 100 A |
| Mobile Phase | Gradient MeCN -40-80%, 30 min |
| Buffer | Ammonium formate pH 3.0 – 20 mM |
| Flow Rate | 1.0 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 50C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Aliphatic sulfonic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium Chloride, Triton X100, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, 1-Hexanesulfonic acid, sodium salt, 1-Heptanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, Sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-Octanesulfonic acid |
Application Column
Newcrom BH
Column Diameter: 4.6 mm
Column Length: 250 mm
Particle Size: 5 µm
Pore Size: 100 A
1-Heptanesulfonic acid
1-Hexanesulfonic acid, sodium salt
1-Octanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Benzalkonium chloride
Cetylpyridinium Chloride
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
Triton X100

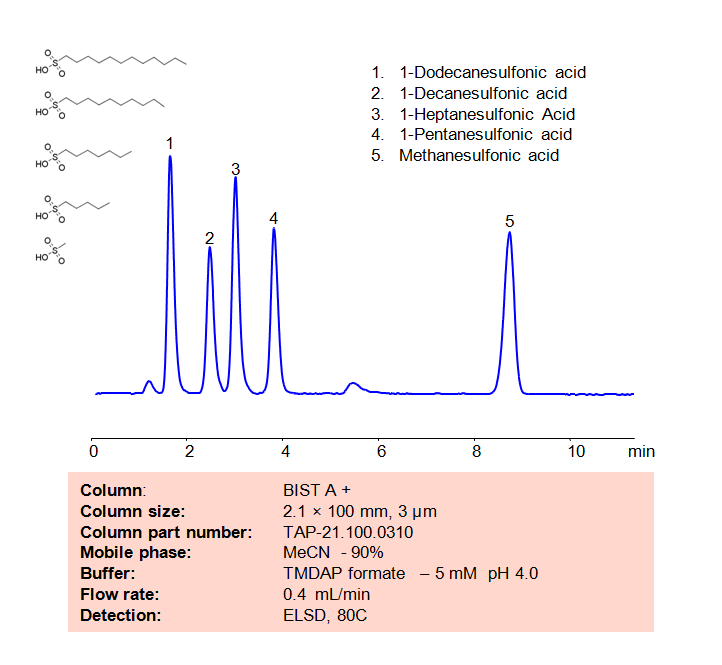
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sulfonic acids on BIST A+ Column
June 16, 2022
Separation type: Bridge Ion Separation Technology, or BIST™ by SIELC Technologies
HPLC Method for Analysis of Sulfonic acids on BIST A+ Column by SIELC Technologies
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Method for Analysis of Sulfonic acid
Methanesulfonic acid is a popular non-volatile catalyst used in organic reactions due to it being a strong acid. Other sulfonic acids, like 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, 1-Heptanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, and 1=Dodecanesulfonic acid are typically used in ion chromatography and for organic syntheses. Using SIELC’s newly introduced BIST™ method, a mixture of these Sulfonic acids can be separated on a negatively-charged, cation-exchange BIST™ A+ column, contrary to conventional chromatographic wisdom. There are two keys to this retention method: 1) a multi-charged, positive buffer, such as N,N,N’,N’-Tetramethyl-1,3-propanediamine (TMDAP), which acts as a bridge, linking the negatively-charged anion analytes to the negatively-charged column surface and 2) a mobile phase consisting mostly of organic solvent (such as MeCN) to minimize the formation of a solvation layer around the charged analytes. Other positively-charged buffers that can generate BIST™ include Calcium acetate and Magnesium acetate. Using this new and unique analysis method, these Sulfonic acids can be separated, retained, and detected through ELSD. This method is also compatible with Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and CAD.
Condition
| Column | BIST™ A+, 2.1×100 mm, 3 µm, 100A |
| Mobile Phase | MeCN – 90% |
| Buffer | TMDAP formate pH 4.0 – 5,0 mM |
| Flow Rate | 0.4 ml/min |
| Detection | ELSD, 80C |
Description
| Class of Compounds | Acid, Sulfonic acid |
| Analyzing Compounds | 1-Dodecanesulfonic acid, 1-Decanesulfonic acid, 1-Heptanesulfonic Acid, 1-Pentanesulfonic acid, Methanesulfonic acid |
Application Column
BIST A+
BIST™ columns offer a unique and effective way to achieve separations that were traditionally challenging or even impossible with other HPLC columns. With the use of a special mobile phase, these ion exchange columns provide very strong retention for analytes with the same charge polarity as the stationary phase, unlocking new chromatography applications. What makes BIST™ columns stand out is their proprietary surface chemistry, which results in superior selectivity, resolution, and sensitivity. These columns offer a simple, efficient solution for a variety of analytical challenges, making them an excellent choice for researchers and analysts across many different fields. To learn more about the technology that powers BIST™ columns and to explore related applications, check out https://BIST.LC.
Select options1-Dodecanesulfonic acid
1-Heptanesulfonic acid
1-Pentanesulfonic acid
Methanesulfonic Acid